Intraocular pressure measurement by three different tonometers in primary congenital glaucoma
- PMID: 26005552
- PMCID: PMC4424718
- DOI: 10.4103/2008-322X.156105
Intraocular pressure measurement by three different tonometers in primary congenital glaucoma
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the agreement between intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements using an automated non-contact tonometer (NCT), Goldmann applanation tonometer (GAT), and the ocular response analyzer (ORA) in subjects with primary congenital glaucoma (PCG).
Methods: Twenty-nine eyes of 17 PCG patients underwent IOP measurements using NCT, GAT and ORA. Variables obtained by the ORA were corneal-compensated IOP (IOPcc), Goldmann-correlated IOP (IOPg), corneal hysteresis (CH), and corneal resistance factor (CRF). A difference more than 1.5 mmHg for IOP was considered as clinically relevant.
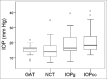
Results: Mean age of the patients was 12 years. Mean IOP (±standard deviation, SD) was 15.3 ± 2.8 mmHg (GAT), 15.5 ± 6.0 (NCT), 19.2 ± 7.0 (IOPg), and 21.1 ± 7.9 (IOPcc); (P = 0.001). Except for NCT vs. GAT (P = 1.0), the average IOP difference between each pair of measurements was clinically relevant. The 95% limits of agreements were - 10.2 to 10.3 mmHg (NCT vs. GAT), -7.8 to 15.3 (IOPg vs. GAT), and - 8.1 to 19.0 (IOPcc vs. GAT). The differences in IOP measurements increased significantly with higher average IOP values (r = 0.715, P = 0.001, for NCT vs. GAT; r = 0.802, P < 0.001, for IOPg vs. GAT; and r = 0.806, P < 0.001, for IOPcc vs. GAT). CH showed a significant association with differences in IOP measurements only for IOPcc vs. GAT (r = 0.830, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Mean IOP obtained by NCT was not significantly different from that of GAT, but ORA measured IOPs were significantly higher than both other devices.
Keywords: Goldmann Applanation Tonometer; Intraocular Pressure; Noncontact Tonometer; Ocular Response Analyzer; Primary Congenital Glaucoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Intraocular pressure measured by dynamic contour tonometer and ocular response analyzer in normal tension glaucoma.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010 Jan;248(1):73-7. doi: 10.1007/s00417-009-1169-4. Epub 2009 Aug 20. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 19693527
-
Intraocular pressure measurement precision with the Goldmann applanation, dynamic contour, and ocular response analyzer tonometers.Ophthalmology. 2010 Apr;117(4):730-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2009.09.020. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Ophthalmology. 2010. PMID: 20122737 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of current tonometry techniques in measurement of intraocular pressure.J Curr Ophthalmol. 2016 Nov 28;29(2):92-97. doi: 10.1016/j.joco.2016.08.010. eCollection 2017 Jun. J Curr Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 28626817 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of intraocular pressure measured by ocular response analyzer and Goldmann applanation tonometer after corneal refractive surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Ophthalmol. 2020 Jan 10;20(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12886-019-1288-6. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 31924174 Free PMC article.
-
How to Measure Intraocular Pressure: An Updated Review of Various Tonometers.J Clin Med. 2021 Aug 27;10(17):3860. doi: 10.3390/jcm10173860. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34501306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Axial Length Changes Following Surgical Intervention in Children With Primary Congenital Glaucoma.Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 1;1:747801. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2021.747801. eCollection 2021. Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 38983968 Free PMC article.
-
Intraocular Pressure Changes after Water Drinking Test in Surgically Treated Primary Congenital Glaucoma.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2020 Aug 6;15(3):318-325. doi: 10.18502/jovr.v15i3.7450. eCollection 2020 Jul-Sep. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2020. PMID: 32864062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Childhood glaucoma profile in Dakahelia, Egypt: a retrospective study.Int J Ophthalmol. 2018 Apr 18;11(4):674-680. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2018.04.23. eCollection 2018. Int J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29675390 Free PMC article.
-
New Approach to the Analysis of Raw Data from the Ocular Response Analyzer.Biomed Hub. 2016 Nov 12;1(3):1-11. doi: 10.1159/000452124. eCollection 2016 Sep-Dec. Biomed Hub. 2016. PMID: 31988891 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Reproducibility of Twenty-Four-Hour Intraocular Pressure Curves in Untreated Patients with Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 14;10(10):e0140206. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140206. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26466325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gilbert C, Rahi J, Quinn G. 2nd ed. London: Edward Arnold Ltd; 2003. Visual impairment and blindness in children.
-
- Beck AD. Diagnosis and management of pediatric glaucoma. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2001;14:501–512. - PubMed
-
- Richardson KT, Jr, Ferguson WJ, Jr, Shaffer RN. Long-term functional results in infantile glaucoma. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1967;71:833–837. - PubMed
-
- Shiose Y. Intraocular pressure: New perspectives. Surv Ophthalmol. 1990;34:413–435. - PubMed
-
- Kotecha A, Elsheikh A, Roberts CR, Zhu H, Garway-Heath DF. Corneal thickness- and age-related biomechanical properties of the cornea measured with the ocular response analyzer. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006;47:5337–5347. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

