Functional cortical neurons and astrocytes from human pluripotent stem cells in 3D culture
- PMID: 26005811
- PMCID: PMC4489980
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.3415
Functional cortical neurons and astrocytes from human pluripotent stem cells in 3D culture
Abstract
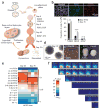
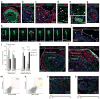
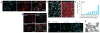
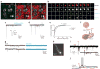
The human cerebral cortex develops through an elaborate succession of cellular events that, when disrupted, can lead to neuropsychiatric disease. The ability to reprogram somatic cells into pluripotent cells that can be differentiated in vitro provides a unique opportunity to study normal and abnormal corticogenesis. Here, we present a simple and reproducible 3D culture approach for generating a laminated cerebral cortex-like structure, named human cortical spheroids (hCSs), from pluripotent stem cells. hCSs contain neurons from both deep and superficial cortical layers and map transcriptionally to in vivo fetal development. These neurons are electrophysiologically mature, display spontaneous activity, are surrounded by nonreactive astrocytes and form functional synapses. Experiments in acute hCS slices demonstrate that cortical neurons participate in network activity and produce complex synaptic events. These 3D cultures should allow a detailed interrogation of human cortical development, function and disease, and may prove a versatile platform for generating other neuronal and glial subtypes in vitro.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
-
- Paşca SP, Panagiotakos G, Dolmetsch RE. Generating human neurons in vitro and using them to understand neuropsychiatric disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2014;37:479–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- F30MH106261/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH094714/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS092474/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS075252/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS075252/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH020016/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01MH100900/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034774/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21MH099797/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH100900/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH099555/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R33 MH087898/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5R37 MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH099797/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS081703/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007365/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS092474/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 MH106261/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01 MH094714/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS007280/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH087898/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM007365/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R56 MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01MH100900-02S1/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH099555-03/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS090911/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

