Development of an RF-EMF Exposure Surrogate for Epidemiologic Research
- PMID: 26006132
- PMCID: PMC4454989
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph120505634
Development of an RF-EMF Exposure Surrogate for Epidemiologic Research
Abstract
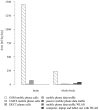
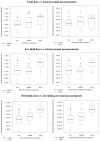
Exposure assessment is a crucial part in studying potential effects of RF-EMF. Using data from the HERMES study on adolescents, we developed an integrative exposure surrogate combining near-field and far-field RF-EMF exposure in a single brain and whole-body exposure measure. Contributions from far-field sources were modelled by propagation modelling and multivariable regression modelling using personal measurements. Contributions from near-field sources were assessed from both, questionnaires and mobile phone operator records. Mean cumulative brain and whole-body doses were 1559.7 mJ/kg and 339.9 mJ/kg per day, respectively. 98.4% of the brain dose originated from near-field sources, mainly from GSM mobile phone calls (93.1%) and from DECT phone calls (4.8%). Main contributors to the whole-body dose were GSM mobile phone calls (69.0%), use of computer, laptop and tablet connected to WLAN (12.2%) and data traffic on the mobile phone via WLAN (6.5%). The exposure from mobile phone base stations contributed 1.8% to the whole-body dose, while uplink exposure from other people's mobile phones contributed 3.6%. In conclusion, the proposed approach is considered useful to combine near-field and far-field exposure to an integrative exposure surrogate for exposure assessment in epidemiologic studies. However, substantial uncertainties remain about exposure contributions from various near-field and far-field sources.
Keywords: RF-EMF; adolescents; dose calculation; exposure assessment; mobile phone.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effect of exposure to radiofrequency fields on cancer risk in the general and working population: A systematic review of human observational studies - Part I: Most researched outcomes.Environ Int. 2024 Sep;191:108983. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2024.108983. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Environ Int. 2024. PMID: 39241333
-
Personal radiofrequency electromagnetic field exposure measurements in Swiss adolescents.Environ Int. 2017 Feb;99:303-314. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2016.12.008. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Environ Int. 2017. PMID: 28038972
-
Radiofrequency electromagnetic fields from mobile communication: Description of modeled dose in brain regions and the body in European children and adolescents.Environ Res. 2021 Feb;193:110505. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110505. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Environ Res. 2021. PMID: 33245886
-
Estimated whole-brain and lobe-specific radiofrequency electromagnetic fields doses and brain volumes in preadolescents.Environ Int. 2020 Sep;142:105808. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105808. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Environ Int. 2020. PMID: 32554140
-
Spatial and temporal RF electromagnetic field exposure of children and adults in indoor micro environments in Belgium and Greece.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013 Nov;113(2):254-63. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23872299 Review.
Cited by
-
Design of an Integrated Platform for Mapping Residential Exposure to Rf-Emf Sources.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jul 24;17(15):5339. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17155339. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32722208 Free PMC article.
-
Symptoms in Swiss adolescents in relation to exposure from fixed site transmitters: a prospective cohort study.Environ Health. 2016 Jul 16;15(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12940-016-0158-4. Environ Health. 2016. PMID: 27422272 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field in the High-Frequency Band and Cognitive Function in Children and Adolescents: A Literature Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Dec 8;17(24):9179. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17249179. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33302600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields on cognitive performance in human experimental studies: A protocol for a systematic review.Environ Int. 2021 Dec;157:106783. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.106783. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Environ Int. 2021. PMID: 34333292 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of exposure to non-ionising electromagnetic fields in the Spanish INMA birth cohort: study protocol.BMC Public Health. 2016 Feb 18;16:167. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-2825-3. BMC Public Health. 2016. PMID: 26892951 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heinrich S., Thomas S., Heumann C., von Kries R., Radon K. Association between exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields assessed by dosimetry and acute symptoms in children and adolescents: A population based cross-sectional study. Environ. Health. 2010 doi: 10.1186/1476-069X-9-75. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

