Estimating a regional ventilation-perfusion index
- PMID: 26006279
- PMCID: PMC4479200
- DOI: 10.1088/0967-3334/36/6/1283
Estimating a regional ventilation-perfusion index
Abstract
This is a methods paper, where an approximation to the local ventilation-perfusion ratio is derived. This approximation, called the ventilation-perfusion index since it is not exactly the physiological ventilation-perfusion ratio, is calculated using conductivity reconstructions obtained using electrical impedance tomography. Since computation of the ventilation-perfusion index only requires knowledge of the internal conductivity, any conductivity reconstruction method may be used. The method is explained and results are presented using conductivities obtained from two EIT systems, one using an iterative method and the other a linearization method.
Figures

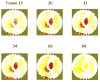
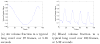
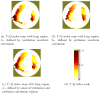
References
-
- Amm B, Kao T-J, Wang X, Boverman G, Shoudy D, Sabatini J, Ashe JM, Newell JC, Isaacson D, Saulnier GJ, Davenport D. Real-Time 3D Electrical Impedance Imaging for Ventilation Monitoring of the lung: Pilot study. IEEE EMBC 36th Conf; Chicago. 2014. - PubMed
-
- Ashe JM, Shoudy D, Boverman G, Sabatini J, Kao T-J, Amm B. A High Precision Parallel Current Drive Experimental EIT System. 15th Int. Conf. Biomed. Appl. EIT; 2014. pp. 24–26.
-
- Blue RS, Isaacson D, Newell JC. Real-time three dimensional electrical impedance imaging. Physiol Meas. 2000;21:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Borges JB, Suarez-Sipmann F, Bohm SH, Tusman G, Melo A, Maripuu E, Sandström M, Park M, Costa ELV, Hedenstierna G, Amato M. Regional lung perfusion estimated by electrical impedance tomography in a piglet model of lung collapse. J Appl Physiol. 2012;112:225–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
