Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Water-Soluble Poly-(ethylene glycol)-10-hydroxycamptothecin Conjugates
- PMID: 26007190
- PMCID: PMC6272474
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules20059393
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Water-Soluble Poly-(ethylene glycol)-10-hydroxycamptothecin Conjugates
Abstract
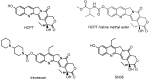
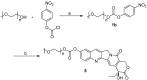
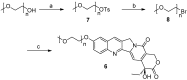
In order to improve the antitumor activity and water solubility of 10-hydroxycamptothecin (HCPT), a series of novel HCPT conjugates were designed and synthesized by conjugating polyethylene glycol (PEG) to the 10-hydroxyl group of HCPT via a valine spacer. The in vitro stability of these synthesized compounds was determined in pH 7.4 buffer at 37 °C, and the results showed that they released HCPT at different rates. All the compounds demonstrated significant antitumor activity in vitro against K562, HepG2 and HT-29 cells. Among them, compounds, 4a, 4d, 4e and 4f, exhibited 2-5 times higher potency than HCPT. The stability and antitumor activity of these conjugates were found to be closely related to the length of PEG and the linker type, conjugates with a relatively short PEG chain and carbamate linkages (compounds 4a and 4f) exhibited controlled release of HCPT and excellent antitumor in vitro activity.
Keywords: PEG; antitumor; conjugate; hydroxycamptothecin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ohwada J., Ozawa S., Kohchi M. Synthesis and biological activities of a pH-dependently activated water-soluble prodrug of a novel hexacyclic camptothecin analog. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009;19:2772–2776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources