Applications of two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy
- PMID: 26007625
- PMCID: PMC4500793
- DOI: 10.1039/c5an00558b
Applications of two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy
Abstract
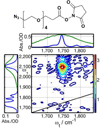
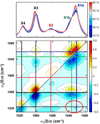
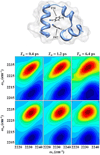
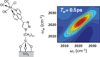
Two-dimensional infrared (2D IR) spectroscopy has recently emerged as a powerful tool with applications in many areas of scientific research. The inherent high time resolution coupled with bond-specific spatial resolution of IR spectroscopy enable direct characterization of rapidly interconverting species and fast processes, even in complex systems found in chemistry and biology. In this minireview, we briefly outline the fundamental principles and experimental procedures of 2D IR spectroscopy. Using illustrative example studies, we explain the important features of 2D IR spectra and their capability to elucidate molecular structure and dynamics. Primarily, this minireview aims to convey the scope and potential of 2D IR spectroscopy by highlighting select examples of recent applications including the use of innate or introduced vibrational probes for the study of nucleic acids, peptides/proteins, and materials.
Figures
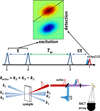
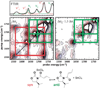
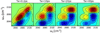
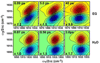


References
-
- Zheng J, Kwak K, Fayer MD. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007;40:75–83. - PubMed
-
- Park S, Kwak K, Fayer MD. Laser Phys. Lett. 2007;4:704–718.
-
- Mukamel S. Principles of Nonlinear Optics and Spectroscopy. New York: Oxford University Press; 1995.
-
- Hamm P, Zanni M. Concepts and Methods of 2D Infrared Spectroscopy. Cambridge University Press; 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

