Two mechanisms coordinate replication termination by the Escherichia coli Tus-Ter complex
- PMID: 26007657
- PMCID: PMC4499146
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv527
Two mechanisms coordinate replication termination by the Escherichia coli Tus-Ter complex
Abstract
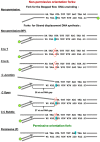
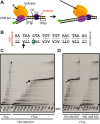
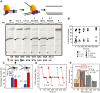
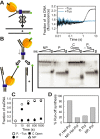
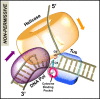
The Escherichia coli replication terminator protein (Tus) binds to Ter sequences to block replication forks approaching from one direction. Here, we used single molecule and transient state kinetics to study responses of the heterologous phage T7 replisome to the Tus-Ter complex. The T7 replisome was arrested at the non-permissive end of Tus-Ter in a manner that is explained by a composite mousetrap and dynamic clamp model. An unpaired C(6) that forms a lock by binding into the cytosine binding pocket of Tus was most effective in arresting the replisome and mutation of C(6) removed the barrier. Isolated helicase was also blocked at the non-permissive end, but unexpectedly the isolated polymerase was not, unless C(6) was unpaired. Instead, the polymerase was blocked at the permissive end. This indicates that the Tus-Ter mechanism is sensitive to the translocation polarity of the DNA motor. The polymerase tracking along the template strand traps the C(6) to prevent lock formation; the helicase tracking along the other strand traps the complementary G(6) to aid lock formation. Our results are consistent with the model where strand separation by the helicase unpairs the GC(6) base pair and triggers lock formation immediately before the polymerase can sequester the C(6) base.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A molecular mousetrap determines polarity of termination of DNA replication in E. coli.Cell. 2006 Jun 30;125(7):1309-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.040. Cell. 2006. PMID: 16814717
-
Differential Tus-Ter binding and lock formation: implications for DNA replication termination in Escherichia coli.Mol Biosyst. 2012 Oct;8(10):2783-91. doi: 10.1039/c2mb25281c. Mol Biosyst. 2012. PMID: 22859262
-
Replication termination in Escherichia coli: structure and antihelicase activity of the Tus-Ter complex.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005 Sep;69(3):501-26. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.69.3.501-526.2005. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16148308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Escherichia coli Tus-Ter replication fork barrier causes site-specific DNA replication perturbation in yeast.Nat Commun. 2014 Apr 7;5:3574. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4574. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 24705096
-
What is all this fuss about Tus? Comparison of recent findings from biophysical and biochemical experiments.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Feb;53(1):49-63. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2017.1394264. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29108427 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA polymerase ε-dependent modulation of the pausing property of the CMG helicase at the barrier.Genes Dev. 2018 Oct 1;32(19-20):1315-1320. doi: 10.1101/gad.317073.118. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Genes Dev. 2018. PMID: 30232092 Free PMC article.
-
Replisome speed determines the efficiency of the Tus-Ter replication termination barrier.Nature. 2015 Sep 17;525(7569):394-8. doi: 10.1038/nature14866. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26322585
-
Xer Site Specific Recombination: Double and Single Recombinase Systems.Front Microbiol. 2017 Mar 20;8:453. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00453. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28373867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryo-EM structure of the replisome reveals multiple interactions coordinating DNA synthesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 7;114(10):E1848-E1856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1701252114. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28223502 Free PMC article.
-
Delineation of the Ancestral Tus-Dependent Replication Fork Trap.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 16;22(24):13533. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413533. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948327 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hiasa H., Marians K.J. Tus prevents overreplication of oriC plasmid DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:26959–26968. - PubMed
-
- Gottlieb P.A., Wu S., Zhang X., Tecklenburg M., Kuempel P., Hill T.M. Equilibrium, kinetic, and footprinting studies of the Tus-Ter protein-DNA interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1992;267:7434–7443. - PubMed
-
- Neylon C., Brown S.E., Kralicek A.V., Miles C.S., Love C.A., Dixon N.E. Interaction of the Escherichia coli replication terminator protein (Tus) with DNA: a model derived from DNA-binding studies of mutant proteins by surface plasmon resonance. Biochemistry. 2000;39:11989–11999. - PubMed
-
- Mulcair M.D., Schaeffer P.M., Oakley A.J., Cross H.F., Neylon C., Hill T.M., Dixon N.E. A molecular mousetrap determines polarity of termination of DNA replication in E. coli. Cell. 2006;125:1309–1319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

