Optimal Self-Tuning PID Controller Based on Low Power Consumption for a Server Fan Cooling System
- PMID: 26007725
- PMCID: PMC4481903
- DOI: 10.3390/s150511685
Optimal Self-Tuning PID Controller Based on Low Power Consumption for a Server Fan Cooling System
Abstract
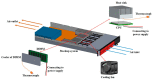
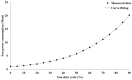
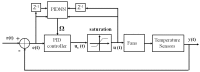
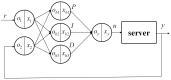
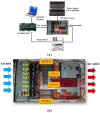
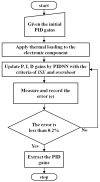
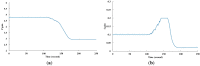
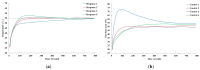
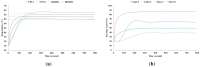
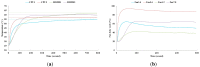
Recently, saving the cooling power in servers by controlling the fan speed has attracted considerable attention because of the increasing demand for high-density servers. This paper presents an optimal self-tuning proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller, combining a PID neural network (PIDNN) with fan-power-based optimization in the transient-state temperature response in the time domain, for a server fan cooling system. Because the thermal model of the cooling system is nonlinear and complex, a server mockup system simulating a 1U rack server was constructed and a fan power model was created using a third-order nonlinear curve fit to determine the cooling power consumption by the fan speed control. PIDNN with a time domain criterion is used to tune all online and optimized PID gains. The proposed controller was validated through experiments of step response when the server operated from the low to high power state. The results show that up to 14% of a server's fan cooling power can be saved if the fan control permits a slight temperature response overshoot in the electronic components, which may provide a time-saving strategy for tuning the PID controller to control the server fan speed during low fan power consumption.
Keywords: PID neural network; fan power model; optimal self-tuning; server fan cooling system.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neural Network-Based Self-Tuning PID Control for Underwater Vehicles.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Sep 5;16(9):1429. doi: 10.3390/s16091429. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27608018 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous gains tuning in boiler/turbine PID-based controller clusters using iterative feedback tuning methodology.ISA Trans. 2012 Sep;51(5):609-21. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2012.04.003. Epub 2012 May 26. ISA Trans. 2012. PMID: 22633781
-
PID controller auto-tuning based on process step response and damping optimum criterion.ISA Trans. 2014 Jan;53(1):85-96. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2013.08.011. Epub 2013 Sep 12. ISA Trans. 2014. PMID: 24035643
-
Metaheuristic algorithms for PID controller parameters tuning: review, approaches and open problems.Heliyon. 2022 May 11;8(5):e09399. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09399. eCollection 2022 May. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35600459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of airflow on the thermal environment and energy efficiency in raised-floor data centers: A review.Sci Total Environ. 2019 Dec 10;695:133801. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133801. Epub 2019 Aug 7. Sci Total Environ. 2019. PMID: 31412303 Review.
Cited by
-
Fractional-Order PID Control Strategy on Hydraulic-Loading System of Typical Electromechanical Platform.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Sep 10;18(9):3024. doi: 10.3390/s18093024. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30201892 Free PMC article.
-
A Low-Cost Chamber Prototype for Automatic Thermal Analysis of MEMS IMU Sensors in Tilt Measurements Perspective.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Jun 16;19(12):2705. doi: 10.3390/s19122705. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31208118 Free PMC article.
-
A FPGA-Based, Granularity-Variable Neuromorphic Processor and Its Application in a MIMO Real-Time Control System.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Aug 23;17(9):1941. doi: 10.3390/s17091941. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28832522 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Tuning Fully-Connected PID Neural Network System for Distributed Temperature Sensing and Control of Instrument with Multi-Modules.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Oct 14;16(10):1709. doi: 10.3390/s16101709. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27754436 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal Compensation of Low-Cost MEMS Accelerometers for Tilt Measurements.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Aug 2;18(8):2536. doi: 10.3390/s18082536. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30072680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lefurgy C., Rajamani K., Rawson F., Felter W., Kistler M., Keller T. Energy Management for Commercial Servers. IEEE Comput. 2003;39:39–48. doi: 10.1109/MC.2003.1250880. - DOI
-
- Patel C.D., Bash C.E., Sharma R., Beitelmam M., Friedrich R.J. Smart Cooling of Data Centers; Proceedings of the Pacific Rim/ASME International Electronic Packaging Technical Conference and Exhibition; Hawaii, HI, USA. 6–11 July 2003; pp. 129–137.
-
- Greenberg S., Mills E., Tschudi B., Rumsey P., Myatt B. Best Practices for Data Centers: Lessons Learned from Benchmarking 22 Data Centers; Proceedings of the ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Buildings; Asilomar, CA, USA. 3 August 2006; pp. 76–87.
-
- Chiueh H., Luh L., Draper J., Choma J. A Novel Fully Integrated Fan Controller for Advanced Computer Systems; Proceedings of the Southwest Symposium on Mixed-Signal Design; San Diego, CA, USA. 27–29 February 2000; pp. 191–194.
-
- Wang Z., Bash C., Tolia N., Marwah M., Zhu X., Ranganathan P. Optimal Fan Speed Control for Thermal Management of Servers; Proceedings of the ASME/Pacific Rim Technical Conference and Exhibition on Packaging and Integration of Electronic and Photonic Systems, MEMS, and NEMS; San Francisco, CA, USA. 19–23 July 2009; pp. 709–719.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

