Role for neonatal D-serine signaling: prevention of physiological and behavioral deficits in adult Pick1 knockout mice
- PMID: 26008737
- PMCID: PMC4661134
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2015.61
Role for neonatal D-serine signaling: prevention of physiological and behavioral deficits in adult Pick1 knockout mice
Abstract
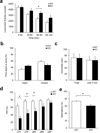
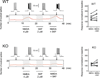
NMDA glutamate receptors have key roles in brain development, function and dysfunction. Regulatory roles of D-serine in NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic plasticity have been reported. Nonetheless, it is unclear whether and how neonatal deficits in NMDA-receptor-mediated neurotransmission affect adult brain functions and behavior. Likewise, the role of D-serine during development remains elusive. Here we report behavioral and electrophysiological deficits associated with the frontal cortex in Pick1 knockout mice, which show D-serine deficits in a neonatal- and forebrain-specific manner. The pathological manifestations observed in adult Pick1 mice are rescued by transient neonatal supplementation of D-serine, but not by a similar treatment in adulthood. These results indicate a role for D-serine in neurodevelopment and provide novel insights on how we interpret data of psychiatric genetics, indicating the involvement of genes associated with D-serine synthesis and degradation, as well as how we consider animal models with neonatal application of NMDA receptor antagonists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

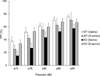

Similar articles
-
D-Serine ameliorates neonatal PolyI:C treatment-induced emotional and cognitive impairments in adult mice.J Pharmacol Sci. 2012;120(3):213-27. doi: 10.1254/jphs.12142fp. Epub 2012 Oct 26. J Pharmacol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23099320
-
Modulation of D-serine levels in brains of mice lacking PICK1.Biol Psychiatry. 2008 May 15;63(10):997-1000. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.09.025. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Biol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18191108 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of sodium benzoate on pre-pulse inhibition deficits and hyperlocomotion in mice after administration of phencyclidine.Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2015 Jun;27(3):159-67. doi: 10.1017/neu.2015.1. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2015. PMID: 25648314
-
Phenotypic characterization of orofacial movement topography in mutants with disruption of amino acid mechanisms: glutamate N2A/B/D [GluRε1/2/4] subtypes and the GABA synthesizing enzyme GAD65.Neuroscience. 2013 Oct 10;250:743-54. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.07.038. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23892010
-
Allosteric modulation of NMDA receptor via elevation of brain glycine and D-serine: the therapeutic potentials for schizophrenia.Pharmacol Ther. 2008 Dec;120(3):317-32. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.08.004. Epub 2008 Aug 27. Pharmacol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18805436 Review.
Cited by
-
Early interventions in risk groups for schizophrenia: what are we waiting for?NPJ Schizophr. 2016 Mar 9;2:16003. doi: 10.1038/npjschz.2016.3. eCollection 2016. NPJ Schizophr. 2016. PMID: 27336054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of ADHD risk genes in extended pedigrees by combining linkage analysis and whole-exome sequencing.Mol Psychiatry. 2020 Sep;25(9):2047-2057. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0210-6. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Mol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 30116028 Free PMC article.
-
D-Serine and Serine Racemase Are Associated with PSD-95 and Glutamatergic Synapse Stability.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Feb 25;10:34. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00034. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26941605 Free PMC article.
-
Increased stereotypy in conditional Cxcr4 knockout mice.Neurosci Res. 2016 Apr;105:75-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Neurosci Res. 2016. PMID: 26458529 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Analysis of PICK1 Gene in Alzheimer's Disease: A Study for Finding a New Gene Target.Front Neurol. 2019 Jan 9;9:1169. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.01169. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30687223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paré D. Presynaptic induction and expression of NMDA-dependent LTP. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:440–441. - PubMed
-
- Anwyl R. Induction and expression mechanisms of postsynaptic NMDA receptor-independent homosynaptic long-term depression. Prog Neurobiol. 2006;78:17–37. - PubMed
-
- Panatier A, Theodosis DT, Mothet JP, Touquet B, Pollegioni L, Poulain DA, et al. Glia-derived D-serine controls NMDA receptor activity and synaptic memory. Cell. 2006;125:775–784. - PubMed
-
- Snyder SH, Kim PM. D-amino acids as putative neurotransmitters: focus on D-serine. Neurochem Res. 2000;25:553–560. - PubMed
-
- Wolosker H. D-serine regulation of NMDA receptor activity. Sci STKE. 2006;2006:pe41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 MH094268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-091387/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-069853/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-092443/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH069853/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083728/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS036715/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH085226/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH091387/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-084018/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-085226/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R56 MH057683/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH057683/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-094268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 MH088753/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH092443/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MH084018/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-083728/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-057683/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-088753/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

