Receptor dimerization dynamics as a regulatory valve for plasticity of type I interferon signaling
- PMID: 26008745
- PMCID: PMC4442803
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201412049
Receptor dimerization dynamics as a regulatory valve for plasticity of type I interferon signaling
Abstract
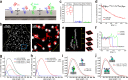
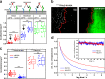
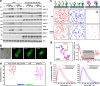
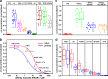
Type I interferons (IFNs) activate differential cellular responses through a shared cell surface receptor composed of the two subunits, IFNAR1 and IFNAR2. We propose here a mechanistic model for how IFN receptor plasticity is regulated on the level of receptor dimerization. Quantitative single-molecule imaging of receptor assembly in the plasma membrane of living cells clearly identified IFN-induced dimerization of IFNAR1 and IFNAR2. The negative feedback regulator ubiquitin-specific protease 18 (USP18) potently interferes with the recruitment of IFNAR1 into the ternary complex, probably by impeding complex stabilization related to the associated Janus kinases. Thus, the responsiveness to IFNα2 is potently down-regulated after the first wave of gene induction, while IFNβ, due to its ∼100-fold higher binding affinity, is still able to efficiently recruit IFNAR1. Consistent with functional data, this novel regulatory mechanism at the level of receptor assembly explains how signaling by IFNβ is maintained over longer times compared with IFNα2 as a temporally encoded cause of functional receptor plasticity.
© 2015 Wilmes et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparable potency of IFNalpha2 and IFNbeta on immediate JAK/STAT activation but differential down-regulation of IFNAR2.Biochem J. 2007 Oct 1;407(1):141-51. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070605. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17627610 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-induced assembling of the type I interferon receptor on supported lipid bilayers.J Mol Biol. 2004 Jul 30;341(1):303-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.059. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15312780
-
The stability of the ternary interferon-receptor complex rather than the affinity to the individual subunits dictates differential biological activities.J Biol Chem. 2008 Nov 21;283(47):32925-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806019200. Epub 2008 Sep 18. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18801736
-
Structural and dynamic determinants of type I interferon receptor assembly and their functional interpretation.Immunol Rev. 2012 Nov;250(1):317-34. doi: 10.1111/imr.12001. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23046138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The receptor of the type I interferon family.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007;316:71-95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-71329-6_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17969444 Review.
Cited by
-
USP18 - a multifunctional component in the interferon response.Biosci Rep. 2018 Nov 15;38(6):BSR20180250. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180250. Print 2018 Dec 21. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30126853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiotherapy resistance driven by Asparagine endopeptidase through ATR pathway modulation in breast cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Feb 27;44(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03334-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40012043 Free PMC article.
-
Surrogate Wnt agonists that phenocopy canonical Wnt and β-catenin signalling.Nature. 2017 May 11;545(7653):234-237. doi: 10.1038/nature22306. Epub 2017 May 3. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28467818 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the IFNγ receptor complex guides design of biased agonists.Nature. 2019 Mar;567(7746):56-60. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0988-7. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Nature. 2019. PMID: 30814731 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity of Type I Interferon-Mediated Responses in Cancer Therapy: From Anti-tumor Immunity to Resistance.Front Oncol. 2018 Aug 21;8:322. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00322. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30186768 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brown R.J., Adams J.J., Pelekanos R.A., Wan Y., McKinstry W.J., Palethorpe K., Seeber R.M., Monks T.A., Eidne K.A., Parker M.W., and Waters M.J.. 2005. Model for growth hormone receptor activation based on subunit rotation within a receptor dimer. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12:814–821. 10.1038/nsmb977 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

