Cannabinoid receptor CB1 regulates STAT3 activity and its expression dictates the responsiveness to SR141716 treatment in human glioma patients' cells
- PMID: 26008966
- PMCID: PMC4558164
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3895
Cannabinoid receptor CB1 regulates STAT3 activity and its expression dictates the responsiveness to SR141716 treatment in human glioma patients' cells
Abstract
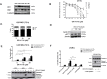
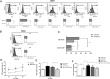
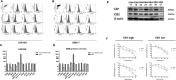
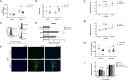
Herein we show that a majority of human brain tumor samples and cell lines over-expressed cannabinoid receptor CB1 as compared to normal human astrocytes (NHA), while uniformly expressed low levels of CB2. This finding prompted us to investigate the therapeutic exploitation of CB1 inactivation by SR141716 treatment, with regard to its direct and indirect cell-mediated effects against gliomas. Functional studies, using U251MG glioma cells and primary tumor cell lines derived from glioma patients expressing different levels of CB1, highlighted SR141716 efficacy in inducing apoptosis via G1 phase stasis and block of TGF-β1 secretion through a mechanism that involves STAT3 inhibition. According to the multivariate role of STAT3 in the immune escape too, interestingly SR141716 lead also to the functional and selective expression of MICA/B on the surface of responsive malignant glioma cells, but not on NHA. This makes SR141716 treated-glioma cells potent targets for allogeneic NK cell-mediated recognition through a NKG2D restricted mechanism, thus priming them for NK cell antitumor reactivity. These results indicate that CB1 and STAT3 participate in a new oncogenic network in the complex biology of glioma and their expression levels in patients dictate the efficacy of the CB1 antagonist SR141716 in multimodal glioma destruction.
Keywords: CB1; MICA; NK cells; STAT3; gliomas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of glioma growth in vivo by selective activation of the CB(2) cannabinoid receptor.Cancer Res. 2001 Aug 1;61(15):5784-9. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11479216
-
The CB1 receptor antagonist rimonabant controls cell viability and ascitic tumour growth in mice.Pharmacol Res. 2012 Mar;65(3):365-71. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2011.11.008. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Pharmacol Res. 2012. PMID: 22123497
-
Recognition by natural killer cells of N6-isopentenyladenosine-treated human glioma cell lines.Int J Cancer. 2018 Jan 1;142(1):176-190. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31036. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 28884474
-
Potential antipsychotic properties of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor antagonists.World J Biol Psychiatry. 2010 Mar;11(2 Pt 2):208-19. doi: 10.3109/15622970801908047. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20218784 Review.
-
Microglia and macrophages in malignant gliomas: recent discoveries and implications for promising therapies.Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:264124. doi: 10.1155/2013/264124. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23864876 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The isoprenoid derivative N6 -benzyladenosine CM223 exerts antitumor effects in glioma patient-derived primary cells through the mevalonate pathway.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Jul;174(14):2287-2301. doi: 10.1111/bph.13824. Epub 2017 Jun 11. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28419419 Free PMC article.
-
The Endocannabinoid System: A Target for Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 23;21(3):747. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030747. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31979368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Wnt/β-Catenin pathway and Histone acetyltransferase activity by Rimonabant: a therapeutic target for colon cancer.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 15;7(1):11678. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11688-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28916833 Free PMC article.
-
STAT3 in the dorsal raphe gates behavioural reactivity and regulates gene networks associated with psychopathology.Mol Psychiatry. 2021 Jul;26(7):2886-2899. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-00904-2. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Mol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33046834 Free PMC article.
-
The endocannabinoid system promotes hepatocyte progenitor cell proliferation and maturation by modulating cellular energetics.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Mar 25;9(1):104. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01400-6. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 36966147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kesari S. Understanding glioblastoma tumor biology: the potential to improve current diagnosis and treatments. Semin Oncol. 2011;38:S2–10. - PubMed
-
- Pisanti S, Picardi P, D'Alessandro A, Laezza C, Bifulco M. The endocannabinoid signaling system in cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013;34:273–82. Review. - PubMed
-
- Velasco G, Sánchez C, Guzmán M. Towards the use of cannabinoids as antitumour agents. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:436–44. - PubMed
-
- Katona I, Freund TF. Endocannabinoid signaling as a synaptic circuit breaker in neurological disease. Nat Med. 2008;14:923–30. - PubMed
-
- Aguado T, Monory K, Palazuelos J, Stella N, Cravatt B, Lutz B, Marsicano G, Kokaia Z, Guzmán M, Galve-Roperh I. The endocannabinoid system drives neural progenitor proliferation. FASEB J. 2005;19:1704–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

