A small-molecule inhibitor suppresses the tumor-associated mitochondrial NAD(P)+-dependent malic enzyme (ME2) and induces cellular senescence
- PMID: 26008970
- PMCID: PMC4652989
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3907
A small-molecule inhibitor suppresses the tumor-associated mitochondrial NAD(P)+-dependent malic enzyme (ME2) and induces cellular senescence
Abstract
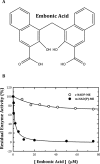
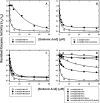
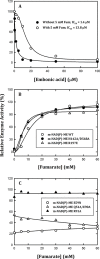
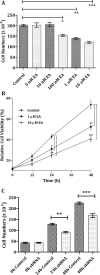
Here, we found a natural compound, embonic acid (EA), that can specifically inhibit the enzymatic activity of mitochondrial NAD(P)+-dependent malic enzyme (m-NAD(P)-ME, ME2) either in vitro or in vivo. The in vitro IC50 value of EA for m-NAD(P)-ME was 1.4 ± 0.4 μM. Mutagenesis and binding studies revealed that the putative binding site of EA on m-NAD(P)-ME is located at the fumarate binding site or at the dimer interface near the site. Inhibition studies reveal that EA displayed a non-competitive inhibition pattern, which demonstrated that the binding site of EA was distinct from the active site of the enzyme. Therefore, EA is thought to be an allosteric inhibitor of m-NAD(P)-ME. Both EA treatment and knockdown of m-NAD(P)-ME by shRNA inhibited the growth of H1299 cancer cells. The protein expression and mRNA synthesis of m-NAD(P)-ME in H1299 cells were not influenced by EA, suggesting that the EA-inhibited H1299 cell growth occurs through the suppression of in vivo m-NAD(P)-ME activity EA treatment further induced the cellular senescence of H1299 cells. However, down-regulation of the enzyme-induced cellular senescence was not through p53. Therefore, the EA-evoked senescence of H1299 cells may occur directly through the inhibition of ME2 or a p53-independent pathway.
Keywords: allosteric inhibitor; cellular senescence; mutagenesis analysis; non-competitive inhibition; selective inhibitor.
Figures


References
-
- Frenkel R. Regulation and physiological function of malic enzyme. Curr Top Cellu Regul. 1975;9:157–181. - PubMed
-
- Chang GG, Tong L. Structure and function of malic enzymes, a new class of oxidative decarboxylases. Biochemistry. 2003;42:12721–12733. - PubMed
-
- Loeber G, Infante AA, maurer-Fogy I, Krystek E, Dworkin MB. Human NAD+-dependent mitochondrial malic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:3016–3021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

