Tumor promotion by γ and suppression by β non-muscle actin isoforms
- PMID: 26008973
- PMCID: PMC4546487
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3989
Tumor promotion by γ and suppression by β non-muscle actin isoforms
Abstract
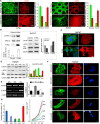
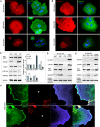
Here we have shown that β-cytoplasmic actin acts as a tumor suppressor, inhibiting cell growth and invasion in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. In contrast, γ-cytoplasmic actin increases the oncogenic potential via ERK1/2, p34-Arc, WAVE2, cofilin1, PP1 and other regulatory proteins. There is a positive feedback loop between γ-actin expression and ERK1/2 activation. We conclude that non-muscle actin isoforms should not be considered as merely housekeeping proteins and the β/γ-actins ratio can be used as an oncogenic marker at least for lung and colon carcinomas. Agents that increase β- and/or decrease γ-actin expression may be useful for anticancer therapy.
Keywords: ERK1/2; PP1; WAVE; actin isoforms; cancer; cofilin1; p34-Arc.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors do not have any conflicts of interests.
Figures






References
-
- Vandekerckhove J, Weber K. At least six different actins are expressed in a higher mammal: an analysis based on the amino acid sequence of the amino-terminal tryptic peptide. J Mol Biol. 1978;126:783–802. - PubMed
-
- Rubenstein PA. The functional importance of multiple actin isoforms. Bioessays. 1990;12:309–315. - PubMed
-
- Harborth J, Elbashir SM, Bechert K, Tuschl T, Weber K. Identification of essential genes in cultured mammalian cells using small interfering RNAs. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:4557–4565. - PubMed
-
- Khaitlina SY. Functional specificity of actin isoforms. Int Rev Cytol. 2001;202:35–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

