D-Galactosamine Intoxication in Experimental Animals: Is it Only an Experimental Model of Acute Liver Failure?
- PMID: 26009004
- PMCID: PMC4451715
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.893291
D-Galactosamine Intoxication in Experimental Animals: Is it Only an Experimental Model of Acute Liver Failure?
Abstract
Background: Short-term administration of Galactosamine to experimental animals causes liver damage and acute liver failure (ALF), as well as acute renal failure in some cases. The aim of our study was to describe kidney disorders that developed in the course of galactosamine-induced liver failure.
Material and methods: Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into 2 groups: a study group administered galactosamine intraperitoneally and a control group administered saline.
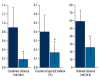
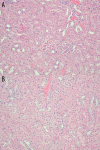
Results: All the animals in the study group developed liver damage and failure within 48 h, with significant increase of alanine (p<0.001), aspartate aminotransferases (p<0.0001), bilirubin (p<0.004), and ammonia (p<0.005) and decrease of albumin (p<0.001) concentrations. Acute renal failure was observed in all test animals, with a significant increase in creatinine (p<0.001) and urea (p<0.001) concentrations and a decrease in creatinine clearance (p<0.0012). Moreover, osmotic clearance (p<0.001), daily natriuresis (p<0.003), and fractional sodium excretion (p<0.016) decreased significantly in this group of animals. The ratio of urine osmolality to serum osmolality did not change. Histopathology of the liver revealed massive necrosis of hepatocytes, whereas renal histopathology showed no changes.
Conclusions: Acute renal failure that developed in the course of galactosamine-induced ALF was of a functional nature, with the kidneys retaining the ability to concentrate urine and retain sodium, and there were no renal changes in the histopathological examination. It seems that the experimental model of ALF induced by galactosamine can be viewed as a model of hepatorenal syndrome that occurs in the course of acute damage and liver failure.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Description of an experimental model of hepatorenal syndrome in Wistar rats].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2004 Aug;17(98):119-22. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2004. PMID: 15603319 Polish.
-
[Race of experimental animals and development of renal failure in animal model of hepatorenal syndrome].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2008 Apr;24(142):298-302. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2008. PMID: 18634359 Polish.
-
[Role of neutrophils in treatment of rats with D-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2016 Aug 20;24(8):601-607. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2016.08.009. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27788708 Chinese.
-
Effect of nitric oxide pathway regulation on water/sodium balance and renal function in a rodent model of acute liver and renal failure.Med Sci Monit. 2014 Sep 27;20:1735-44. doi: 10.12659/MSM.890757. Med Sci Monit. 2014. PMID: 25270512 Free PMC article.
-
Salvage effect of E5564, Toll-like receptor 4 antagonist on d-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver failure in rats.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 May;25(5):1009-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.06145.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 20546456
Cited by
-
Prevention and Therapeutic Effects and Mechanisms of Tanshinone IIA Sodium Sulfonate on Acute Liver Injury Mice Model.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:4097398. doi: 10.1155/2016/4097398. Epub 2016 May 4. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27274751 Free PMC article.
-
Recent developments in in vitro and in vivo models for improved translation of preclinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics data.Drug Metab Rev. 2021 May;53(2):207-233. doi: 10.1080/03602532.2021.1922435. Epub 2021 May 25. Drug Metab Rev. 2021. PMID: 33989099 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-induced-acute liver failure: A critical appraisal of the thioacetamide model for the study of hepatic encephalopathy.Toxicol Rep. 2021 Apr 30;8:962-970. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.04.011. eCollection 2021. Toxicol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34026559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipoic acid as a protective agent against lipopolysaccharide and other natural toxins: a comprehensive review.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 14. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04123-w. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40227307 Review.
-
Protective Effects of the Third Generation Vasodilatory Βeta - Blocker Nebivolol against D-Galactosamine - Induced Hepatorenal Syndrome in Rats.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017 Dec 13;5(7):880-892. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2017.173. eCollection 2017 Dec 15. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29362613 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keppler D, Lesch R, Reutter W, Decker K. Experimental hepatitis induced by D-galactosamine. Exp Mol Pathol. 1968;9:279–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

