Are cyclooxygenase-2 and nitric oxide involved in the dyskinesia of Parkinson's disease induced by L-DOPA?
- PMID: 26009769
- PMCID: PMC4455759
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2014.0190
Are cyclooxygenase-2 and nitric oxide involved in the dyskinesia of Parkinson's disease induced by L-DOPA?
Abstract
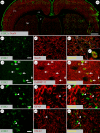
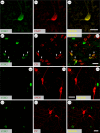
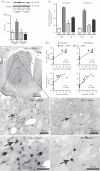
Inflammatory mechanisms are proposed to play a role in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2) contributes to inflammation pathways in the periphery and is constitutively expressed in the central nervous system. Considering that inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) formation attenuates L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia, this study aimed at investigating if a NO synthase (NOS) inhibitor would change COX2 brain expression in animals with L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. To this aim, male Wistar rats received unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine microinjection into the medial forebrain bundle were treated daily with L-DOPA (21 days) combined with 7-nitroindazole or vehicle. All hemi-Parkinsonian rats receiving l-DOPA showed dyskinesia. They also presented increased neuronal COX2 immunoreactivity in the dopamine-depleted dorsal striatum that was directly correlated with dyskinesia severity. Striatal COX2 co-localized with choline-acetyltransferase, calbindin and DARPP-32 (dopamine-cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein-32), neuronal markers of GABAergic neurons. NOS inhibition prevented L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia and COX2 increased expression in the dorsal striatum. These results suggest that increased COX2 expression after L-DOPA long-term treatment in Parkinsonian-like rats could contribute to the development of dyskinesia.
Keywords: COX2; extrasynaptic signalling; neuroinflammation; prostaglandin H-synthase; striatum interneurons; volume transmission.
© 2015 The Author(s) Published by the Royal Society. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibition attenuates the development of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in hemi-Parkinsonian rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 May 15;683(1-3):166-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.03.008. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22449381
-
Glial activation is associated with l-DOPA induced dyskinesia and blocked by a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in a rat model of Parkinson's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Jan;73:377-87. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.10.017. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 25447229
-
Anti-dyskinetic effect of the neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor is linked to decrease of FosB/deltaFosB expression.Neurosci Lett. 2013 Apr 29;541:126-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.02.015. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 23428503
-
l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease: Are neuroinflammation and astrocytes key elements?Synapse. 2016 Dec;70(12):479-500. doi: 10.1002/syn.21941. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Synapse. 2016. PMID: 27618286 Review.
-
Role of nitric oxide in motor control: implications for Parkinson's disease pathophysiology and treatment.Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(5):471-88. doi: 10.2174/138161211795164176. Curr Pharm Des. 2011. PMID: 21375483 Review.
Cited by
-
Antidyskinetic Effect of 7-Nitroindazole and Sodium Nitroprusside Associated with Amantadine in a Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease.Neurotox Res. 2016 Jul;30(1):88-100. doi: 10.1007/s12640-016-9618-4. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Neurotox Res. 2016. PMID: 27053252
-
Effects of hydrogen gas inhalation on L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2023 Apr 8;30:100623. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2023.100623. eCollection 2023 Jul. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2023. PMID: 37096172 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol Alleviates Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia in Rats.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 25;12:683577. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.683577. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34248967 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabidiol and Cannabinoid Compounds as Potential Strategies for Treating Parkinson's Disease and L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia.Neurotox Res. 2020 Jan;37(1):12-29. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-00109-8. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Neurotox Res. 2020. PMID: 31637586 Review.
-
4'-fluorocannabidiol associated with capsazepine restrains L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in hemiparkinsonian mice: Contribution of anti-inflammatory and anti-glutamatergic mechanisms.Neuropharmacology. 2024 Jun 15;251:109926. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.109926. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Neuropharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38554815 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

