Serotonin release from the neuronal cell body and its long-lasting effects on the nervous system
- PMID: 26009775
- PMCID: PMC4455765
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2014.0196
Serotonin release from the neuronal cell body and its long-lasting effects on the nervous system
Abstract
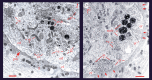
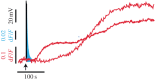
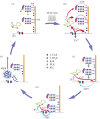
Serotonin, a modulator of multiple functions in the nervous system, is released predominantly extrasynaptically from neuronal cell bodies, axons and dendrites. This paper describes how serotonin is released from cell bodies of Retzius neurons in the central nervous system (CNS) of the leech, and how it affects neighbouring glia and neurons. The large Retzius neurons contain serotonin packed in electrodense vesicles. Electrical stimulation with 10 impulses at 1 Hz fails to evoke exocytosis from the cell body, but the same number of impulses at 20 Hz promotes exocytosis via a multistep process. Calcium entry into the neuron triggers calcium-induced calcium release, which activates the transport of vesicle clusters to the plasma membrane. Exocytosis occurs there for several minutes. Serotonin that has been released activates autoreceptors that induce an inositol trisphosphate-dependent calcium increase, which produces further exocytosis. This positive feedback loop subsides when the last vesicles in the cluster fuse and calcium returns to basal levels. Serotonin released from the cell body is taken up by glia and released elsewhere in the CNS. Synchronous bursts of neuronal electrical activity appear minutes later and continue for hours. In this way, a brief train of impulses is translated into a long-term modulation in the nervous system.
Keywords: extrasynaptic; neuron–glia communication; serotonergic modulation; serotonin; somatic exocytosis; transmitter release.
Figures
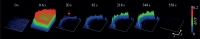
Similar articles
-
The Thermodynamically Expensive Contribution of Three Calcium Sources to Somatic Release of Serotonin.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 28;23(3):1495. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031495. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biophysics of active vesicle transport, an intermediate step that couples excitation and exocytosis of serotonin in the neuronal soma.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e45454. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045454. Epub 2012 Oct 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23056204 Free PMC article.
-
Exocytosis of serotonin from the neuronal soma is sustained by a serotonin and calcium-dependent feedback loop.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Jun 27;8:169. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00169. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25018697 Free PMC article.
-
Extrasynaptic Communication.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Apr 30;14:638858. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.638858. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33994942 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic and extrasynaptic secretion of serotonin.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2005 Mar;25(2):297-312. doi: 10.1007/s10571-005-3061-z. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16047543 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Label-free imaging of neurotransmitters in live brain tissue by multi-photon ultraviolet microscopy.Neuronal Signal. 2018 Dec 3;2(4):NS20180132. doi: 10.1042/NS20180132. eCollection 2018 Dec. Neuronal Signal. 2018. PMID: 32714595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional profiling of identified neurons in leech.BMC Genomics. 2021 Mar 25;22(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07526-0. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33765928 Free PMC article.
-
The Thermodynamically Expensive Contribution of Three Calcium Sources to Somatic Release of Serotonin.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 28;23(3):1495. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031495. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the Basis of Synaptic Integration Constancy during Growth of a Neuronal Circuit.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Aug 18;10:198. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00198. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27587998 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating Like a Fly: Drosophila melanogaster as a Model to Explore the Contribution of Serotonergic Neurotransmission to Spatial Navigation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 23;24(5):4407. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054407. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901836 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

