Hypoxia promotes colon cancer dissemination through up-regulation of cell migration-inducing protein (CEMIP)
- PMID: 26009875
- PMCID: PMC4653038
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3978
Hypoxia promotes colon cancer dissemination through up-regulation of cell migration-inducing protein (CEMIP)
Abstract
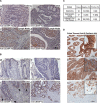
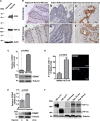
Hypoxic stress drives cancer progression by causing a transcriptional reprogramming. Recently, KIAA1199 was discovered to be a cell-migration inducing protein (renamed CEMIP) that is upregulated in human cancers. However, the mechanism of induction of CEMIP in cancer was hitherto unknown. Here we demonstrate that hypoxia induces CEMIP expression leading to enhanced cell migration. Immunohistochemistry of human colon cancer tissues revealed that CEMIP is upregulated in cancer cells located at the invasive front or in the submucosa. CEMIP localization inversely correlated with E-cadherin expression, which is characteristic of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Mechanistically, hypoxia-inducible-factor-2α (HIF-2α), but not HIF-1α binds directly to the hypoxia response element within the CEMIP promoter region resulting in increased CEMIP expression. Functional characterization reveals that CEMIP is a downstream effector of HIF-2α-mediated cell migration. Expression of CEMIP was demonstrated to negatively correlate with the expression of Jarid1A, a histone demethylase that removes methyl groups from H3K4me3 (an activation marker for transcription), resulting in altered gene repression. Low oxygen tension inhibits the function of Jarid1A, leading to increased presence of H3K4me3 within the CEMIP promoter. These results provide insight into the upregulation of CEMIP within cancer and can lead to novel treatment strategies targeting this cancer cell migration-promoting gene.
Keywords: HIF-2α; KIAA1199/CEMIP; invasion; migration.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dexamethasone inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colon cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Sep 14;21(34):9887-99. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9887. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26379394 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 2α Facilitates the Progression of Colon Tumors through Recruiting Neutrophils.Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Feb 15;37(5):e00481-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00481-16. Print 2017 Mar 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 27956697 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia increases KIAA1199/CEMIP expression and enhances cell migration in pancreatic cancer.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 14;11(1):18193. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97752-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34521918 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CEMIP in cancers and its transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation.PeerJ. 2024 Feb 19;12:e16930. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16930. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38390387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The crucial role of CEMIP in cancer metastasis: Mechanistic insights and clinical implications.FASEB J. 2025 Jan 15;39(1):e70284. doi: 10.1096/fj.202402522R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 39758005 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-6 increases matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP-14) levels via down-regulation of p53 to drive cancer progression.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 20;7(38):61107-61120. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11243. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27531896 Free PMC article.
-
CEMIP, a Promising Biomarker That Promotes the Progression and Metastasis of Colorectal and Other Types of Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 18;14(20):5093. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205093. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TMEM2: A missing link in hyaluronan catabolism identified?Matrix Biol. 2019 May;78-79:139-146. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.03.020. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Matrix Biol. 2019. PMID: 29601864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KIAA1199 promotes migration and invasion by Wnt/β-catenin pathway and MMPs mediated EMT progression and serves as a poor prognosis marker in gastric cancer.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 19;12(4):e0175058. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175058. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28422983 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of genomic, transcriptomic and functional profiles of aggressive osteosarcomas across multiple species.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 25;8(44):76241-76256. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19532. eCollection 2017 Sep 29. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29100308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matsuzaki S, Tanaka F, Mimori K, Tahara K, Inoue H, Mori M. Clinicopathologic significance of KIAA1199 overexpression in human gastric cancer. Annals of surgical oncology. 2009;16:2042–2051. - PubMed
-
- Sabates-Bellver J, Van der Flier LG, de Palo M, Cattaneo E, Maake C, Rehrauer H, Laczko E, Kurowski MA, Bujnicki JM, Menigatti M, Luz J, Ranalli TV, Gomes V, Pastorelli A, Faggiani R, Anti M, et al. Transcriptome profile of human colorectal adenomas. Molecular cancer research: MCR. 2007;5:1263–1275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

