Phosphorylation of interleukin (IL)-24 is required for mediating its anti-cancer activity
- PMID: 26009991
- PMCID: PMC4599269
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3977
Phosphorylation of interleukin (IL)-24 is required for mediating its anti-cancer activity
Abstract
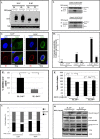
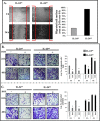
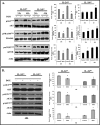
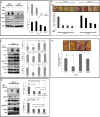
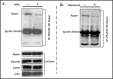
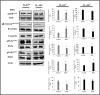
Interleukin (IL)-24 is a tumor suppressor/cytokine gene that undergoes post-translational modifications (PTMs). Glycosylation and ubiquitination are important for IL-24 protein stabilization and degradation respectively. Little is known about IL-24 protein phosphorylation and its role in IL-24-mediated anti-tumor activities. In this study we conducted molecular studies to determine whether IL-24 phosphorylation is important for IL-24-mediated anti-cancer activity.Human H1299 lung tumor cell line that was stably transfected with a doxycycline (DOX)-inducible (Tet-on) plasmid vector carrying the cDNA of IL-24-wild-type (IL-24wt) or IL-24 with all five phosphorylation sites replaced (IL-24mt) was used in the present study. Inhibition of tumor cell proliferation, cell migration and invasion, and induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest was observed in DOX-induced IL-24wt-expressing cells but not in IL-24mt-expressing cells. Secretion of IL-24mt protein was greatly reduced compared to IL-24wt protein. Further, IL-24wt and IL-24mt proteins markedly differed in their subcellular organelle localization. IL-24wt but not IL-24mt inhibited the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. SiRNA-mediated AKT knockdown and overexpression of myristolyated AKT protein confirmed that IL-24wt but not IL-24mt mediated its anti-cancer activity by inhibiting the AKT signaling pathway.Our results demonstrate that IL-24 phosphorylation is required for inhibiting the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and exerting its anti-cancer activities.
Keywords: IL-24; cytokine; lung cancer; phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-24 inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by disrupting the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling axis.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 16;10(3):e0122439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122439. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25775124 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing the FOLR2 Gene Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Increases Apoptosis in the NCI-H1650 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Line via Inhibition of AKT/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR)/Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase 1 (S6K1) Signaling.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Nov 11;24:8064-8073. doi: 10.12659/MSM.911384. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30415267 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling pathway induces resistance to the apoptotic activities of SCH66336 (lonafarnib) through Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin-mediated increases in survivin expression.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Mar 1;14(5):1581-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0952. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18316583
-
IL-22 induced cell proliferation is regulated by PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling cascade.Cytokine. 2012 Oct;60(1):38-42. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.06.316. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Cytokine. 2012. PMID: 22840496
-
Inhibition of 14-3-3 binding to Rictor of mTORC2 for Akt phosphorylation at Ser473 is regulated by selenoprotein W.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1833(10):2135-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.05.005. Epub 2013 May 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23680186
Cited by
-
Interleukin (IL)-24: Reconfiguring the Tumor Microenvironment for Eliciting Antitumor Response.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1290:99-110. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-55617-4_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33559858
-
miR-203a-3p.1 targets IL-24 to modulate hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth and metastasis.FEBS Open Bio. 2017 Jul 10;7(8):1085-1091. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12248. eCollection 2017 Aug. FEBS Open Bio. 2017. PMID: 28781949 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of Her2/Neu mammary tumor development in mda-7/IL-24 transgenic mice.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 10;6(35):36943-54. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6046. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26460950 Free PMC article.
-
IL-24 modulates the high mobility group (HMG) A1/miR222 /AKT signaling in lung cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 25;7(43):70247-70263. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11838. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27602961 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 24 Promotes Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Glucose Regulation, and Apoptosis by Inactivating Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta in Human Prostate Cancer Cells.Cells. 2025 Feb 28;14(5):357. doi: 10.3390/cells14050357. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40072085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jiang H, Lin JJ, Su ZZ, Goldstein NI, Fisher PB. Subtraction hybridization identifies a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human melanoma differentiation, growth and progression. Oncogene. 1995;11:2477–2486. - PubMed
-
- Caudell EG, Mumm JB, Poindexter N, Ekmekcioglu S, Mhashilkar AM, Yang XH, Retter MW, Hill P, Chada S, Grimm EA. The protein product of the tumor suppressor gene, melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7, exhibits immunostimulatory activity and is designated IL-24. J Immunol. 2002;168:6041–6046. - PubMed
-
- Saeki T, Mhashilkar A, Swanson X, Zou-Yang XH, Sieger K, Kawabe S, Branch CD, Zumstein L, Meyn RE, Roth JA, Chada S, Ramesh R. Inhibition of human lung cancer growth following adenovirus-mediated mda-7 gene expression in vivo. Oncogene. 2002;21:4558–4566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

