The First High-Density Genetic Map Construction in Tree Peony (Paeonia Sect. Moutan) using Genotyping by Specific-Locus Amplified Fragment Sequencing
- PMID: 26010095
- PMCID: PMC4444326
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128584
The First High-Density Genetic Map Construction in Tree Peony (Paeonia Sect. Moutan) using Genotyping by Specific-Locus Amplified Fragment Sequencing
Abstract
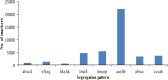
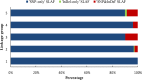
Genetic linkage maps, permitting the elucidation of genome structure, are one of most powerful genomic tools to accelerate marker-assisted breeding. However, due to a lack of sufficient user-friendly molecular markers, no genetic linkage map has been developed for tree peonies (Paeonia Sect. Moutan), a group of important horticultural plants worldwide. Specific-locus amplified fragment sequencing (SLAF-seq) is a recent molecular marker development technology that enable the large-scale discovery and genotyping of sequence-based marker in genome-wide. In this study, we performed SLAF sequencing of an F1 population, derived from the cross P. ostti 'FenDanBai' × P. × suffruticosa 'HongQiao', to identify sufficient high-quality markers for the construction of high-density genetic linkage map in tree peonies. After SLAF sequencing, a total of 78 Gb sequencing data and 285,403,225 pair-end reads were generated. We detected 309,198 high-quality SLAFs from these data, of which 85,124 (27.5%) were polymorphic. Subsequently, 3518 of the polymorphic markers, which were successfully encoded in to Mendelian segregation types, and were in conformity with the criteria of high-quality markers, were defined as effective markers and used for genetic linkage mapping. Finally, we constructed an integrated genetic map, which comprised 1189 markers on the five linkage groups, and spanned 920.699 centiMorgans (cM) with an average inter-marker distance of 0.774 cM. There were 1115 'SNP-only' markers, 18 'InDel-only' markers, and 56 'SNP&InDel' markers on the map. Among these markers, 450 (37.85%) showed significant segregation distortion (P < 0.05). In conclusion, this investigation reported the first large-scale marker development and high-density linkage map construction for tree peony. The results of this study will serve as a solid foundation not only for marker-assisted breeding, but also for genome sequence assembly for tree peony.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
High-density genetic map construction and QTLs identification for plant height in white jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) using specific locus amplified fragment (SLAF) sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2017 May 8;18(1):355. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3712-8. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28482802 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a high-density genetic map and the X/Y sex-determining gene mapping in spinach based on large-scale markers developed by specific-locus amplified fragment sequencing (SLAF-seq).BMC Genomics. 2017 Apr 4;18(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3659-9. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28376721 Free PMC article.
-
An SNP-based saturated genetic map and QTL analysis of fruit-related traits in cucumber using specific-length amplified fragment (SLAF) sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2014 Dec 22;15(1):1158. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1158. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25534138 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing consolidates molecular markers with plant breeding practice.Theor Appl Genet. 2015 May;128(5):779-95. doi: 10.1007/s00122-015-2499-8. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Theor Appl Genet. 2015. PMID: 25821196 Review.
-
Linkage maps of human chromosomes.Genome. 1989;31(2):1066-72. doi: 10.1139/g89-183. Genome. 1989. PMID: 2698824 Review.
Cited by
-
A High-Resolution Linkage Map Construction and QTL Analysis for Morphological Traits in Anthurium (Anthurium andraeanum Linden).Plants (Basel). 2023 Dec 17;12(24):4185. doi: 10.3390/plants12244185. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38140512 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a high-density genetic map by specific locus amplified fragment sequencing (SLAF-seq) and its application to Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) analysis for boll weight in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum.).BMC Plant Biol. 2016 Apr 11;16:79. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0741-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 27067834 Free PMC article.
-
Association mapping for floral traits in cultivated Paeonia rockii based on SSR markers.Mol Genet Genomics. 2017 Feb;292(1):187-200. doi: 10.1007/s00438-016-1266-0. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Mol Genet Genomics. 2017. PMID: 27807670
-
Surveying the genome and constructing a high-density genetic map of napiergrass (Cenchrus purpureus Schumach).Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 26;8(1):14419. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32674-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30258215 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of the first high-density genetic linkage map and identification of seed yield-related QTLs and candidate genes in Elymus sibiricus, an important forage grass in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.BMC Genomics. 2019 Nov 14;20(1):861. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6254-4. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31726988 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li JJ, Zhang XF, Zhao XQ (2011) Tree Peony of China Beijing: Encyclopaedia of China Publishing House. 206 p.
-
- Cheng FY (2007) Advances in the breeding of tree peonies and a cultivar system for the cultivar group. International Journal for Plant Breeding 1(2): 89–104.
-
- Hong DY, Pan KY (2005) Notes on taxonomy of Paeonia sect. Moutan DC. (Paeoniaceae). Acta Phytotax Sin 43(2): 169–177.
-
- Rogers A, Engstrom L (1995) Peonies. Portland: Timber Press. 296 p.
-
- Wang LY (1998) Chinese Tree Peony. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House. 212 p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

