Mitochondrial quality control pathways as determinants of metabolic health
- PMID: 26010263
- PMCID: PMC5053262
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.201500013
Mitochondrial quality control pathways as determinants of metabolic health
Abstract
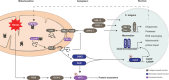
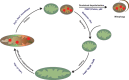
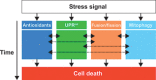
Mitochondrial function is key for maintaining cellular health, while mitochondrial failure is associated with various pathologies, including inherited metabolic disorders and age-related diseases. In order to maintain mitochondrial quality, several pathways of mitochondrial quality control have evolved. These systems monitor mitochondrial integrity through antioxidants, DNA repair systems, and chaperones and proteases involved in the mitochondrial unfolded protein response. Additional regulation of mitochondrial function involves dynamic exchange of components through mitochondrial fusion and fission. Sustained stress induces a selective autophagy - termed mitophagy - and ultimately leads to apoptosis. Together, these systems form a network that acts on the molecular, organellar, and cellular level. In this review, we highlight how these systems are regulated in an integrated context- and time-dependent network of mitochondrial quality control that is implicated in healthy aging.
Keywords: ROS; fission; fusion; mitochondrial dynamics; mitochondrial quality control; mitohormesis; mitophagy.
© 2015 The Authors. Bioessays published by WILEY Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Ryan MT, Hoogenraad NJ. 2007. Mitochondrial‐nuclear communications. Annu Rev Biochem 76: 701–22. - PubMed
-
- Gray MW, Burger G, Lang BF. 1999. Mitochondrial evolution. Science 283: 1476–81. - PubMed
-
- Harbauer AB, Zahedi RP, Sickmann A, Pfanner N, et al. 2014. The protein import machinery of mitochondria‐a regulatory hub in metabolism, stress, and disease. Cell Metab 19: 357–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

