Objective assessment of changes in physical activity and sedentary behavior: Pre- through 3 years post-bariatric surgery
- PMID: 26010326
- PMCID: PMC4445467
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.21106
Objective assessment of changes in physical activity and sedentary behavior: Pre- through 3 years post-bariatric surgery
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate change in sedentary behavior (SB) and physical activity (PA) over 3 years following bariatric surgery.
Methods: A subset of participants in an observational study (n = 473 of 2,458; 79% female, median body mass index 45 kg m(-2) ) wore an activity monitor presurgery and at 1-3 annual postsurgery assessments.
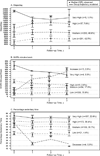
Results: Over the first year, on average, sedentary time decreased from 573 (95% CI: 563-582) to 545 (95% CI: 534-555) min days(-1) and moderate- to vigorous-intensity PA (MVPA) increased from 77 (95% CI: 71-84) to 106 (95% CI: 98-116) min week(-1) , or 7 (95% CI: 5-10) to 24 (95% CI: 18-29) min week(-1) in MVPA bouts ≥10 min. There were no changes in these parameters from years 1 to 3 (P for all > 0.05). The percentage of participants achieving ≥150 min week(-1) of bout-related MVPA was not different at year 3 [6.5% (95% CI: 3.1-12.7)] vs. presurgery [3.4% (95% CI: 1.8-5.0); P = 0.45]. Most participants followed SB and PA trajectories that paralleled mean change and were consistent with their presurgery position in relation to the group.
Conclusions: On average, bariatric surgical patients make small reductions in SB and increases in PA during the first postsurgery year, which are maintained through 3 years. Still, postsurgery PA levels fall short of PA guidelines for general health or weight control.
© 2015 The Obesity Society.
Figures
References
-
- Danielsen KK, Svendsen M, Maehlum S, Sundgot-Borgen J. Changes in body composition, cardiovascular disease risk factors, and eating behavior after an intensive lifestyle intervention with high volume of physical activity in severely obese subjects: a prospective clinical controlled trial. J Obes. 2013;2013:325–464. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ling H, Lenz TL, Burns TL, Hilleman DE. Reducing the risk of obesity: defining the role of weight loss drugs. Pharmacotherapy. 2013;33(12):1308–1321. - PubMed
-
- Higa K, Ho T, Tercero F, Yunus T, Boone KB. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: 10-year follow-up. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011;7(4):516–525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 DK066555/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK66526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00037/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024996/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK066585/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK066557/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK066568/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK066526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000037/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK66471/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK66585/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK66667/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 01-DK66555/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR024996/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK066667/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK66568/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK066471/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000457/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical