High Throughput Sequencing of Small RNAs in the Two Cucurbita Germplasm with Different Sodium Accumulation Patterns Identifies Novel MicroRNAs Involved in Salt Stress Response
- PMID: 26010449
- PMCID: PMC4444200
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127412
High Throughput Sequencing of Small RNAs in the Two Cucurbita Germplasm with Different Sodium Accumulation Patterns Identifies Novel MicroRNAs Involved in Salt Stress Response
Abstract
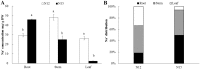
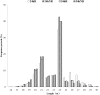
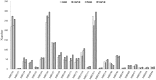
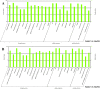
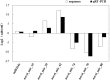
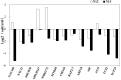
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a class of small non-coding RNAs, recognize their mRNA targets based on perfect sequence complementarity. MiRNAs lead to broader changes in gene expression after plants are exposed to stress. High-throughput sequencing is an effective method to identify and profile small RNA populations in non-model plants under salt stresses, significantly improving our knowledge regarding miRNA functions in salt tolerance. Cucurbits are sensitive to soil salinity, and the Cucurbita genus is used as the rootstock of other cucurbits to enhance salt tolerance. Several cucurbit crops have been used for miRNA sequencing but salt stress-related miRNAs in cucurbit species have not been reported. In this study, we subjected two Cucurbita germplasm, namely, N12 (Cucurbita. maxima Duch.) and N15 (Cucurbita. moschata Duch.), with different sodium accumulation patterns, to Illumina sequencing to determine small RNA populations in root tissues after 4 h of salt treatment and control. A total of 21,548,326 and 19,394,108 reads were generated from the control and salt-treated N12 root tissues, respectively. By contrast, 19,108,240 and 20,546,052 reads were obtained from the control and salt-treated N15 root tissues, respectively. Fifty-eight conserved miRNA families and 33 novel miRNAs were identified in the two Cucurbita germplasm. Seven miRNAs (six conserved miRNAs and one novel miRNAs) were up-regulated in salt-treated N12 and N15 samples. Most target genes of differentially expressed novel miRNAs were transcription factors and salt stress-responsive proteins, including dehydration-induced protein, cation/H+ antiporter 18, and CBL-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase. The differential expression of miRNAs between the two Cucurbita germplasm under salt stress conditions and their target genes demonstrated that novel miRNAs play an important role in the response of the two Cucurbita germplasm to salt stress. The present study initially explored small RNAs in the response of pumpkin to salt stress, and provided valuable information on novel miRNAs and their target genes in Cucurbita.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Small RNA deep sequencing reveals the important role of microRNAs in the halophyte Halostachys caspica.Plant Biotechnol J. 2015 Apr;13(3):395-408. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12337. Plant Biotechnol J. 2015. PMID: 25832169
-
Grafting-responsive miRNAs in cucumber and pumpkin seedlings identified by high-throughput sequencing at whole genome level.Physiol Plant. 2014 Aug;151(4):406-22. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12122. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Physiol Plant. 2014. PMID: 24279842
-
High-throughput deep sequencing shows that microRNAs play important roles in switchgrass responses to drought and salinity stress.Plant Biotechnol J. 2014 Apr;12(3):354-66. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12142. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Plant Biotechnol J. 2014. PMID: 24283289
-
MicroRNA: a new target for improving plant tolerance to abiotic stress.J Exp Bot. 2015 Apr;66(7):1749-61. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv013. Epub 2015 Feb 19. J Exp Bot. 2015. PMID: 25697792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keep calm and carry on: miRNA biogenesis under stress.Plant J. 2019 Sep;99(5):832-843. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14369. Epub 2019 May 23. Plant J. 2019. PMID: 31025462 Review.
Cited by
-
An early ABA-induced stomatal closure, Na+ sequestration in leaf vein and K+ retention in mesophyll confer salt tissue tolerance in Cucurbita species.J Exp Bot. 2018 Sep 14;69(20):4945-4960. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery251. J Exp Bot. 2018. PMID: 29992291 Free PMC article.
-
New technologies accelerate the exploration of non-coding RNAs in horticultural plants.Hortic Res. 2017 Jul 5;4:17031. doi: 10.1038/hortres.2017.31. eCollection 2017. Hortic Res. 2017. PMID: 28698797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and Functional Characterization of Plant MiRNA Under Salt Stress Shed Light on Salinity Resistance Improvement Through MiRNA Manipulation in Crops.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jun 17;12:665439. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.665439. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34220888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A genome-wide identification of the miRNAome in response to salinity stress in date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.).Front Plant Sci. 2015 Nov 5;6:946. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00946. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26594218 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic Expression of Pumpkin NAC Transcription Factor CmNAC1 Improves Multiple Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Arabidopsis.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Nov 28;8:2052. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.02052. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 29234347 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

