Regulation of α5 and αV Integrin Expression by GDF-5 and BMP-7 in Chondrocyte Differentiation and Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 26010756
- PMCID: PMC4443976
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127166
Regulation of α5 and αV Integrin Expression by GDF-5 and BMP-7 in Chondrocyte Differentiation and Osteoarthritis
Abstract
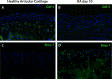
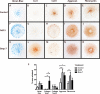
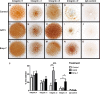
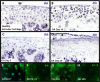
The Integrin β1 family is the major receptors of the Extracellular matrix (ECM), and the synthesis and degradation balance of ECM is seriously disrupted during Osteoarthritis (OA). In this scenario, integrins modify their pattern expression and regulate chondrocyte differentiation in the articular cartilage. Members of the Transforming growth factor beta (Tgf-β) Superfamily, such as Growth differentiation factor 5 (Gdf-5) and Bone morphogenetic protein 7 (Bmp-7), play a key role in joint formation and could regulate the integrin expression during chondrocyte differentiation and osteoarthritis progression in an experimental OA rat model. Decrease of α5 integrin expression in articular cartilage was related with chondrocyte dedifferentiation during OA progression, while increase of α1, α2, and α3 integrin expression was related with fibrous areas in articular cartilage during OA. Hypertrophic chondrocytes expressed αV integrin and was increased in the articular cartilage of rats with OA. Integrin expression during chondrocyte differentiation was also analyzed in a micromass culture system of mouse embryo mesenchymal cells, micromass cultures was treated with Gdf-5 or Bmp-7 for 4 and 6 days, respectively. Gdf-5 induced the expression of the α5 sub-unit, while Bmp-7 induced the expression of the αV sub-unit. This suggests a switch in signaling for prehypertrophic chondrocyte differentiation towards hypertrophy, where Gdf-5 could maintain the articular chondrocyte phenotype and Bmp-7 would induce hypertrophy. Decrease of Ihh expression during late stages of OA in rat model suggest that the ossification in OA rat knees and endochondral ossification could be activated by Bmp-7 and αV integrin in absence of Ihh. Thus, chondrocyte phenotype in articular cartilage is similar to prehypetrophic chondrocyte in growth plate, and is preserved due to the presence of Indian hedgehog (Ihh), Gdf-5 and α5 integrin to maintain articular cartilage and prevent hypertrophy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
TGF-β1/WISP1/Integrin-α interaction mediates human chondrocytes dedifferentiation.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Sep;24(17):8675-8684. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202009_22804. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32964955
-
BAPX-1/NKX-3.2 acts as a chondrocyte hypertrophy molecular switch in osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 Nov;67(11):2944-56. doi: 10.1002/art.39293. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26245691
-
SnoN suppresses maturation of chondrocytes by mediating signal cross-talk between transforming growth factor-β and bone morphogenetic protein pathways.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 17;287(34):29101-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.349415. Epub 2012 Jul 5. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22767605 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulatory Role of Signaling Crosstalk in Hypertrophy of MSCs and Human Articular Chondrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Aug 14;16(8):19225-47. doi: 10.3390/ijms160819225. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26287176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indian Hedgehog, a critical modulator in osteoarthritis, could be a potential therapeutic target for attenuating cartilage degeneration disease.Connect Tissue Res. 2014 Aug;55(4):257-61. doi: 10.3109/03008207.2014.925885. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Connect Tissue Res. 2014. PMID: 24844414 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of BMP Signaling in Endothelial Heterogeneity.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 21;9:673396. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.673396. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34235147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrins, cadherins and channels in cartilage mechanotransduction: perspectives for future regeneration strategies.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2021 Oct 27;23:e14. doi: 10.1017/erm.2021.16. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34702419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From mesenchymal niches to engineered in vitro model systems: Exploring and exploiting biomechanical regulation of vertebrate hedgehog signalling.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Nov 22;17:100502. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100502. eCollection 2022 Dec 15. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 36457847 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of chondrocyte plasticity via connexin43 modulation attenuates cellular senescence and fosters a pro-regenerative environment in osteoarthritis.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Dec 5;9(12):1166. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1225-2. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30518918 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of biological pathways and genes associated with neurogenic heterotopic ossification by text mining.PeerJ. 2020 Jan 3;8:e8276. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8276. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 31915578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buckwalter JA, Mankin HJ, Grodzinsky AJ. Articular cartilage and osteoarthritis. 1st ed. Am Acad Orthop Surg; 1999. - PubMed
-
- Eerola I, Salminen H, Lammi P, Lammi M, Mark Von Der K, Vuorio E, et al. Type X collagen, a natural component of mouse articular cartilage: association with growth, aging, and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998; 41: 1287–1295. 10.1002/1529-0131(199807)41:7<1287::AID-ART20>3.0.CO;2-D - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002; 110: 673–687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

