Uterine NDRG2 expression is increased at implantation sites during early pregnancy in mice, and its down-regulation inhibits decidualization of mouse endometrial stromal cells
- PMID: 26013399
- PMCID: PMC4447025
- DOI: 10.1186/s12958-015-0047-7
Uterine NDRG2 expression is increased at implantation sites during early pregnancy in mice, and its down-regulation inhibits decidualization of mouse endometrial stromal cells
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Uterine NDRG2 expression is increased at implantation sites during early pregnancy in mice, and its down-regulation inhibits decidualization of mouse endometrial stromal cells.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2015 Aug 29;13:98. doi: 10.1186/s12958-015-0089-x. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26319599 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: N-myc down-regulated gene 2 (NDRG2) is a tumor suppressor involved in cell proliferation and differentiation. The aim of this study was to determine the uterine expression pattern of this gene during early pregnancy in mice.
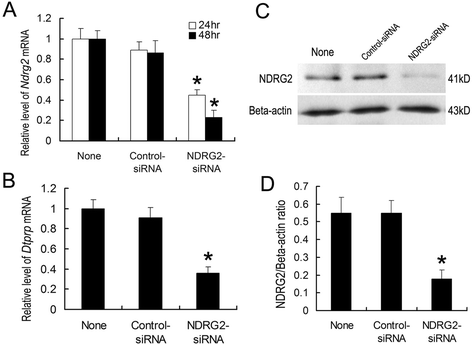
Methods: Uterine NDRG2 mRNA and protein expression levels were determined by RT-PCR and Western blot analyses, respectively, during the peri-implantation period in mice. Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis was performed to examine the spatial localization of NDRG2 expression in mouse uterine tissues. The in vitro decidualization model of mouse endometrial stromal cells (ESCs) was used to evaluate decidualization of ESCs following NDRG2 knock down by small interfering RNA (siRNA). Statistical significance was analyzed by one-way ANOVA using SPSS 19.0 software.
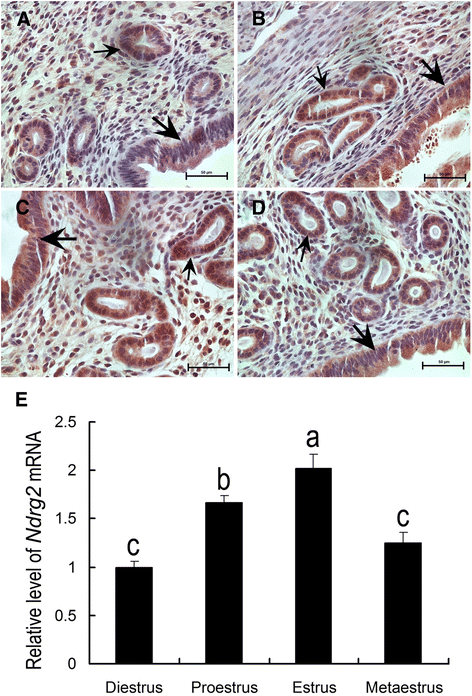
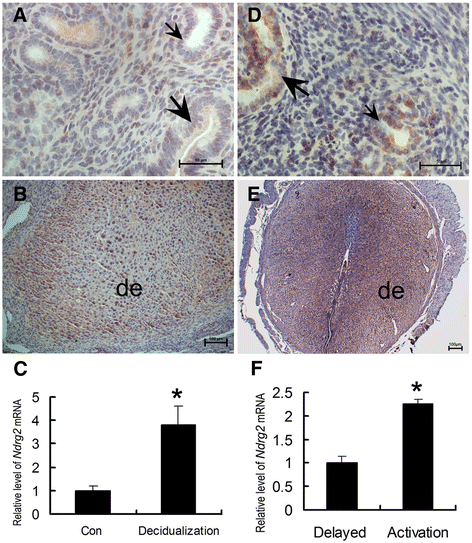
Results: Uterine NDRG2 gene expression was significantly up-regulated and was predominantly localized to the secondary decidual zone on days 5 and 8 of pregnancy in mice. Its increased expression was associated with artificial decidualization as well as the activation of delayed implantation. Furthermore, uterine NDRG2 expression was induced by estrogen and progesterone treatments. The in vitro decidualization of mouse ESCs was accompanied by up-regulation of NDRG2 expression, and knock down of its expression in these cells by siRNA inhibited the decidualization process.
Conclusions: These results suggest that NDRG2 might play an important role in the process of decidualization during early pregnancy.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

