Evaluation of 3D multi-contrast joint intra- and extracranial vessel wall cardiovascular magnetic resonance
- PMID: 26013973
- PMCID: PMC4446075
- DOI: 10.1186/s12968-015-0143-z
Evaluation of 3D multi-contrast joint intra- and extracranial vessel wall cardiovascular magnetic resonance
Abstract
Background: Multi-contrast vessel wall cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) has demonstrated its capability for atherosclerotic plaque morphology measurement and component characterization in different vasculatures. However, limited coverage and partial volume effect with conventional two-dimensional (2D) techniques might cause lesion underestimation. The aim of this work is to evaluate the performance in a) blood suppression and b) vessel wall delineation of three-dimensional (3D) multi-contrast joint intra- and extracranial vessel wall imaging at 3T.
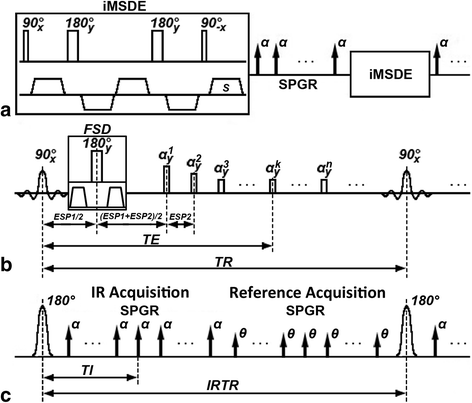
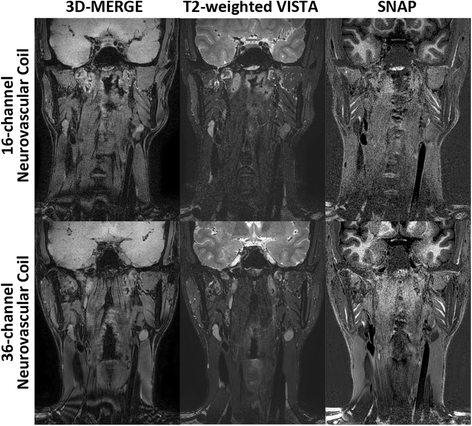
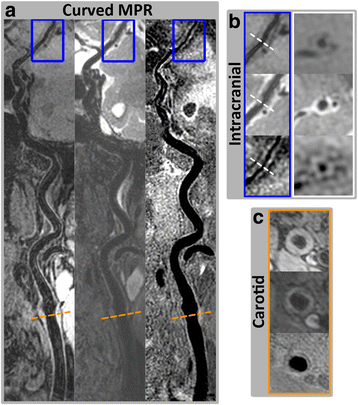
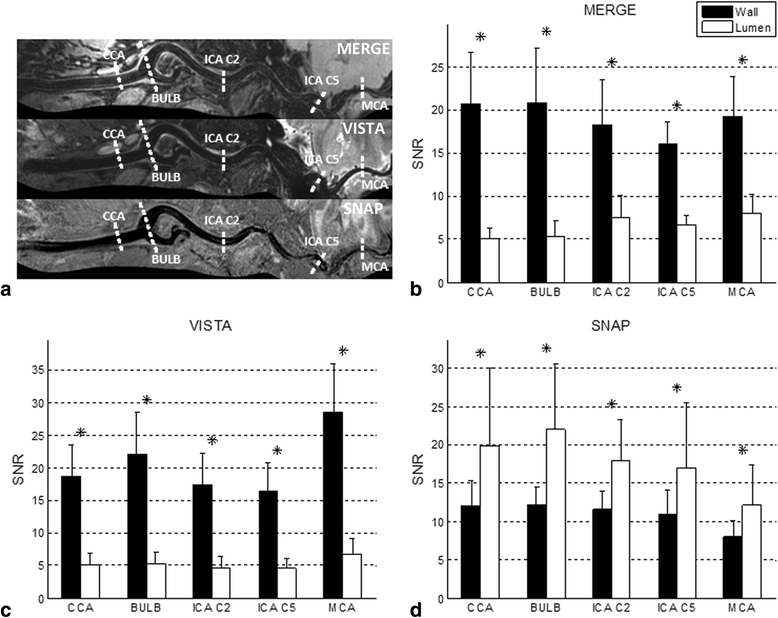
Methods: Three multi-contrast 3D black blood (BB) sequences with T1, T2 and heavy T1 weighting and a custom designed 36-channel neurovascular coil covering the entire intra- and extracranial vasculature have been used and investigated in this study. Two healthy subjects were recruited for sequence parameter optimization and twenty-five patients were consecutively scanned for image quality and blood suppression assessment. Qualitative image scores of vessel wall delineation as well as quantitative Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and Contrast-to-Noise Ratio (CNR) were evaluated at five typical locations ranging from common carotid arteries to middle cerebral arteries.
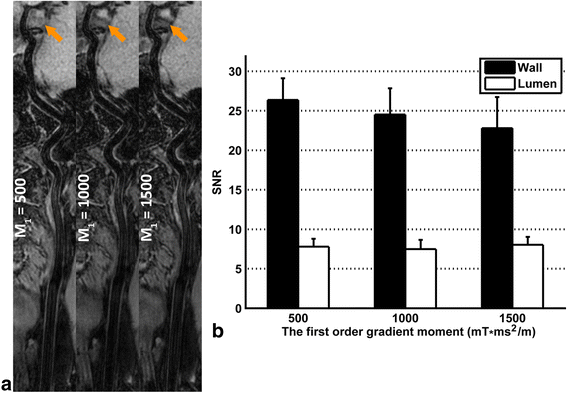
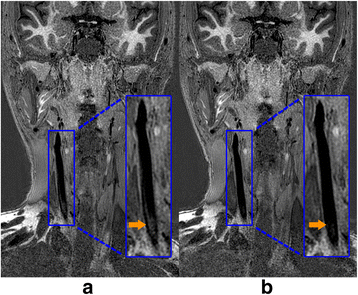
Results: The 3D multi-contrast images acquired within 15mins allowed the vessel wall visualization with 0.8 mm isotropic spatial resolution covering intra- and extracranial segments. Quantitative wall and lumen SNR measurements for each sequence showed effective blood suppression at all selected locations (P < 0.0001). Although the wall-lumen CNR varied across measured locations, each sequence provided good or adequate image quality in both intra- and extracranial segments.
Conclusions: The proposed 3D multi-contrast vessel wall technique provides isotropic resolution and time efficient solution for joint intra- and extracranial vessel wall CMR.
Figures




Similar articles
-
High resolution simultaneous imaging of intracranial and extracranial arterial wall with improved cerebrospinal fluid suppression.Magn Reson Imaging. 2017 Dec;44:65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2017.08.004. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Magn Reson Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28807750
-
Dual stack black blood carotid artery CMR at 3T: application to wall thickness visualization.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2009 Nov 10;11(1):45. doi: 10.1186/1532-429X-11-45. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2009. PMID: 19903348 Free PMC article.
-
3D whole-brain vessel wall cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging: a study on the reliability in the quantification of intracranial vessel dimensions.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2018 Jun 14;20(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12968-018-0453-z. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2018. PMID: 29898736 Free PMC article.
-
Extracranial carotid MR imaging at 3T.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2006 Feb;14(1):109-21. doi: 10.1016/j.mric.2005.12.003. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2006. PMID: 16530639 Review.
-
Three-Dimensional Carotid Plaque MR Imaging.Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2016 Feb;26(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.nic.2015.09.001. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2016. PMID: 26610656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of severity between carotid and intracranial artery atherosclerosis.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018 Jun 4;5(7):843-849. doi: 10.1002/acn3.590. eCollection 2018 Jul. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30009201 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of 3D multi-contrast carotid vessel wall MRI: a comparative study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020 Jan;10(1):269-282. doi: 10.21037/qims.2019.09.11. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020. PMID: 31956548 Free PMC article.
-
Vulnerable carotid plaque characteristics on magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging: potential predictors for hemodynamic instability during carotid artery stenting.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Jun 1;13(6):3441-3450. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-865. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 37284123 Free PMC article.
-
Shape and Location of Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaque and Intraplaque Hemorrhage: A High-resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019 Aug 1;26(8):720-727. doi: 10.5551/jat.47449. Epub 2019 Jan 9. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019. PMID: 30626781 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative assessment of carotid artery atherosclerosis by three-dimensional magnetic resonance and two-dimensional ultrasound imaging: a comparison study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020 May;10(5):1021-1032. doi: 10.21037/qims-19-818. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020. PMID: 32489926 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

