Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Activity of a Novel Anti-PD-L1 Antibody Avelumab (MSB0010718C) on Human Tumor Cells
- PMID: 26014098
- PMCID: PMC4739754
- DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0059
Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Activity of a Novel Anti-PD-L1 Antibody Avelumab (MSB0010718C) on Human Tumor Cells
Abstract
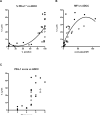
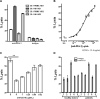
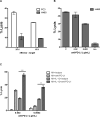
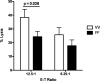
Several anti-PD-1/PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies (mAb) are currently providing evidence of clinical benefit in subsets of cancer patients. The mode of action of these mAbs is to inhibit PD-1 on immune cells interacting with PD-L1 on tumor cells. These mAbs are either designed or engineered to eliminate antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), which, however, has been implicated as an important mechanism in several highly effective mAb-mediated cancer therapies. A fully human anti-PD-L1 mAb would potentially be able to block PD-1/PD-L1 interactions and also mediate the ADCC lysis of tumor cells. MSB0010718C (designated avelumab) is a fully human IgG1 anti-PD-L1 mAb. The studies reported here demonstrate (i) the ability of avelumab to lyse a range of human tumor cells in the presence of PBMC or NK effectors; (ii) IFNγ can enhance tumor cell PD-L1 expression and, in some cases, enhance ADCC tumor cell lysis; (iii) purified NK cells are potent effectors for avelumab; (iv) similar levels of avelumab-mediated ADCC lysis of tumor cells are seen using purified NK as effectors from either healthy donors or cancer patients; (v) very low levels of avelumab-mediated lysis are seen using whole PBMCs as targets; this finding complements results seen in analyses of PBMC subsets of patients receiving avelumab; and (vi) the addition of IL12 to NK cells greatly enhances avelumab-mediated ADCC. These studies thus provide an additional mode of action for an anti-PD-L1 mAb and support the rationale for further studies to enhance avelumab-mediated ADCC activity.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
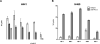
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

