Determinants of phubbing, which is the sum of many virtual addictions: a structural equation model
- PMID: 26014669
- PMCID: PMC4500886
- DOI: 10.1556/2006.4.2015.005
Determinants of phubbing, which is the sum of many virtual addictions: a structural equation model
Abstract
Background and aims: Phubbing can be described as an individual looking at his or her mobile phone during a conversation with other individuals, dealing with the mobile phone and escaping from interpersonal communication. In this research, determinants of phubbing behavior were investigated; in addition, the effects of gender, smart phone ownership and social media membership were tested as moderators.
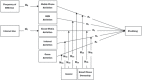
Methods: To examine the cause-effect relations among the variables of the theoretical model, the research employs a correlational design. Participants were 409 university students who were selected via random sampling. Phubbing was obtained via the scales featuring mobile phone addiction, SMS addiction, internet addiction, social media addiction and game addiction. The obtained data were analyzed using a correlation analysis, multiple linear regression analysis and structural equation model.
Results: The results showed that the most important determinants of phubbing behavior are mobile phone, SMS, social media and internet addictions.
Discussion: Although the findings show that the highest correlation value explaining phubbing is a mobile phone addiction, the other correlation values reflect a dependency on the phone.
Conclusions: There is an increasing tendency towards mobile phone use, and this tendency prepares the basis of phubbing.
Keywords: Internet; addiction; mobile phone; phubber; phubbing; social media; structural equation model.
Figures
References
-
- Akçay H. (2011). Social media use with the context of uses and gratification: A research on Gumushane University. Journal of Communication Theory and Research, 33, 138–161.
-
- Amerikan Psikiyatri Birliği (1995). Mental bozuklukların tanısal ve sayımsal elkitabı: DSM-IV, E. Köroğlu (çev.) Ankara: Hekimler Yayın Birliği.
-
- Anderson J. C. & Gerbing D. (1984). The effect of sampling error on convergence, improper solutions, and goodness-of-fit indices for maximum likelihood confirmatory factor analysis. Psychometrika, 49, 155–173.
-
- Andreassen C. S., Torsheim T., Brunborg G. S. & Pallesen S. (2012). Development of a Facebook addiction scale 1, 2. Psychological reports, 110(2), 501–517. - PubMed
-
- Balcı Ş. & Gülnar B. (2009). Internet addiction among university students and the profile of internet addicts. Journal of Selcuk Communication, 6(1), 5–22.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources