Integrated genomic analysis suggests MLL3 is a novel candidate susceptibility gene for familial nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 26014803
- PMCID: PMC4526396
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-15-0275
Integrated genomic analysis suggests MLL3 is a novel candidate susceptibility gene for familial nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Little is known about genetic factors associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). To gain insight into NPC etiology, we performed whole exome sequencing on germline and tumor DNA from three closely related family members with NPC.
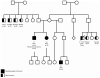
Methods: The family was ascertained through the Pediatric Familial Cancer Clinic at The University of Chicago (Chicago, IL). The diagnosis of NPC was confirmed pathologically for each individual. For each sample sequenced, 97.3% of the exome was covered at 5×, with an average depth of 44×. Candidate germline and somatic variants associated with NPC were identified and prioritized using a custom pipeline.
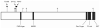
Results: We discovered 72 rare deleterious germline variants in 56 genes shared by all three individuals. Of these, only three are in previously identified NPC-associated genes, all of which are located within MLL3, a gene known to be somatically altered in NPC. One variant introduces an early stop codon in MLL3, which predicts complete loss-of-function. Tumor DNA analysis revealed somatic mutations and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) integration events; none, however, were shared among all three individuals.
Conclusions: These data suggest that inherited mutations in MLL3 may have predisposed these three individuals from a single family to develop NPC, and may cooperate with individually acquired somatic mutations or EBV integration events in NPC etiology.
Impact: Our finding is the first instance of a plausible candidate high penetrance inherited mutation predisposing to NPC.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Whole-exome sequencing identifies MST1R as a genetic susceptibility gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Mar 22;113(12):3317-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1523436113. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26951679 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitation of DNA methylation in Epstein-Barr virus-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma by bisulfite amplicon sequencing.BMC Cancer. 2017 Jul 17;17(1):489. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3482-3. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28716111 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Exome Sequencing Study of Familial Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and Its Implication for Identifying High-Risk Individuals.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022 Dec 8;114(12):1689-1697. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djac177. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022. PMID: 36066420
-
Genetic and epigenetic landscape of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Chin Clin Oncol. 2016 Apr;5(2):16. doi: 10.21037/cco.2016.03.06. Chin Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27121876 Review.
-
Genetic susceptibility to the endemic form of NPC.Chin Clin Oncol. 2016 Apr;5(2):15. doi: 10.21037/cco.2016.03.11. Chin Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27121875 Review.
Cited by
-
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Progression: Accumulating Genomic Instability and Persistent Epstein-Barr Virus Infection.Curr Oncol. 2022 Aug 23;29(9):6035-6052. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29090475. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36135044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of IGFBP3 is associated with poor prognosis and tumor metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Nov;37(11):15043-15052. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5400-8. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27658775
-
Integrated genomic analyses in PDX model reveal a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor Palbociclib as a novel candidate drug for nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 20;37(1):233. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0873-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30236142 Free PMC article.
-
Germline Variants Associated with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Predisposition Identified through Whole-Exome Sequencing.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 28;14(15):3680. doi: 10.3390/cancers14153680. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35954343 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of KMT2C/MLL3 in human colorectal cancer cells reinforces genome-wide H3K4me1 profiles and influences cell growth and gene expression.Clin Epigenetics. 2020 May 29;12(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13148-020-00863-z. Clin Epigenetics. 2020. PMID: 32471474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang ET, Adami HO. The enigmatic epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention : a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive Oncology. 2006;15:1765–77. - PubMed
-
- Eduardo B, Raquel C, Rui M. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a south European population: epidemiological data and clinical aspects in Portugal. European archives of oto-rhino-laryngology : official journal of the European Federation of Oto-Rhino-Laryngological Societies. 2010;267:1607–12. - PubMed
-
- Ward MH, Pan WH, Cheng YJ, Li FH, Brinton LA, Chen CJ, et al. Dietary exposure to nitrite and nitrosamines and risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Taiwan. International journal of cancer Journal international du cancer. 2000;86:603–9. - PubMed

