RX-P873, a Novel Protein Synthesis Inhibitor, Accumulates in Human THP-1 Monocytes and Is Active against Intracellular Infections by Gram-Positive (Staphylococcus aureus) and Gram-Negative (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) Bacteria
- PMID: 26014952
- PMCID: PMC4505283
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00428-15
RX-P873, a Novel Protein Synthesis Inhibitor, Accumulates in Human THP-1 Monocytes and Is Active against Intracellular Infections by Gram-Positive (Staphylococcus aureus) and Gram-Negative (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) Bacteria
Abstract
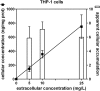
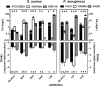
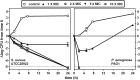
The pyrrolocytosine RX-P873, a new broad-spectrum antibiotic in preclinical development, inhibits protein synthesis at the translation step. The aims of this work were to study RX-P873's ability to accumulate in eukaryotic cells, together with its activity against extracellular and intracellular forms of infection by Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, using a pharmacodynamic approach allowing the determination of maximal relative efficacies (Emax values) and bacteriostatic concentrations (Cs values) on the basis of Hill equations of the concentration-response curves. RX-P873's apparent concentration in human THP-1 monocytes was about 6-fold higher than the extracellular one. In broth, MICs ranged from 0.125 to 0.5 mg/liter (S. aureus) and 2 to 8 mg/liter (P. aeruginosa), with no significant shift in these values against strains resistant to currently used antibiotics being noted. In concentration-dependent experiments, the pharmacodynamic profile of RX-P873 was not influenced by the resistance phenotype of the strains. Emax values (expressed as the decrease in the number of CFU from that in the initial inoculum) against S. aureus and P. aeruginosa reached more than 4 log units and 5 log units in broth, respectively, and 0.7 log unit and 2.7 log units in infected THP-1 cells, respectively, after 24 h. Cs values remained close to the MIC in all cases, making RX-P873 more potent than antibiotics to which the strains were resistant (moxifloxacin, vancomycin, and daptomycin for S. aureus; ciprofloxacin and ceftazidime for P. aeruginosa). Kill curves in broth showed that RX-P873 was more rapidly bactericidal against P. aeruginosa than against S. aureus. Taken together, these data suggest that RX-P873 may constitute a useful alternative for infections involving intracellular bacteria, especially Gram-negative species.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In vitro activity of RX-P873 against Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter baumannii.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Apr;59(4):2280-5. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04840-14. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25645834 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular activity of the peptide antibiotic NZ2114: studies with Staphylococcus aureus and human THP-1 monocytes, and comparison with daptomycin and vancomycin.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010 Aug;65(8):1720-4. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq159. Epub 2010 Jun 9. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20534628
-
In-vitro investigation of the antibacterial activity of agents which may be used for the oral treatment of lung infections in CF patients.J Antimicrob Chemother. 1998 Aug;42(2):171-8. doi: 10.1093/jac/42.2.171. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1998. PMID: 9738834
-
In-vitro profile of a new beta-lactam, ceftobiprole, with activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007 Jun;13 Suppl 2:17-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01722.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007. PMID: 17488372 Review.
-
Review of resistance of ocular isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and staphylococci from keratitis to ciprofloxacin, gentamicin and cephalosporins.Clin Exp Optom. 2011 Mar;94(2):161-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1444-0938.2010.00536.x. Epub 2010 Nov 17. Clin Exp Optom. 2011. PMID: 21083760 Review.
Cited by
-
Lactobacillus acidophilus (strain Scav) postbiotic metabolites reduce infection and modulate inflammation in an in vivo model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa wound infection.J Appl Microbiol. 2025 Mar 3;136(3):lxaf061. doi: 10.1093/jambio/lxaf061. J Appl Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40068933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kanyo Z, Devito J, Bhattacharjee A, Ippolito J, Wimberly B, Duffy E. 2011. Structural basis for the binding of RX-04, a novel broad spectrum antibacterial class, to bacterial ribosomes, abstr ILF1-1842 Abstr 51st Intersci Conf Antimicrob Agents Chemother, Chicago, IL. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

