Upregulation of ER Signaling as an Adaptive Mechanism of Cell Survival in HER2-Positive Breast Tumors Treated with Anti-HER2 Therapy
- PMID: 26015514
- PMCID: PMC4558260
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2728
Upregulation of ER Signaling as an Adaptive Mechanism of Cell Survival in HER2-Positive Breast Tumors Treated with Anti-HER2 Therapy
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the direct effect and therapeutic consequences of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-targeting therapy on expression of estrogen receptor (ER) and Bcl2 in preclinical models and clinical tumor samples.
Experimental design: Archived xenograft tumors from two preclinical models (UACC812 and MCF7/HER2-18) treated with ER and HER2-targeting therapies and also HER2+ clinical breast cancer specimens collected in a lapatinib neoadjuvant trial (baseline and week 2 posttreatment) were used. Expression levels of ER and Bcl2 were evaluated by immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis. The effects of Bcl2 and ER inhibition, by ABT-737 and fulvestrant, respectively, were tested in parental versus lapatinib-resistant UACC812 cells in vitro.
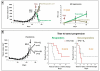
Results: Expression of ER and Bcl2 was significantly increased in xenograft tumors with acquired resistance to anti-HER2 therapy compared with untreated tumors in both preclinical models (UACC812: ER P = 0.0014; Bcl2 P < 0.001 and MCF7/HER2-18: ER P = 0.0007; Bcl2 P = 0.0306). In the neoadjuvant clinical study, lapatinib treatment for 2 weeks was associated with parallel upregulation of ER and Bcl2 (Spearman coefficient: 0.70; P = 0.0002). Importantly, 18% of tumors originally ER-negative (ER(-)) converted to ER(+) upon anti-HER2 therapy. In ER(-)/HER2(+) MCF7/HER2-18 xenografts, ER reexpression was primarily observed in tumors responding to potent combination of anti-HER2 drugs. Estrogen deprivation added to this anti-HER2 regimen significantly delayed tumor progression (P = 0.018). In the UACC812 cells, fulvestrant, but not ABT-737, was able to completely inhibit anti-HER2-resistant growth (P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: HER2 inhibition can enhance or restore ER expression with parallel Bcl2 upregulation, representing an ER-dependent survival mechanism potentially leading to anti-HER2 resistance.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Different mechanisms for resistance to trastuzumab versus lapatinib in HER2-positive breast cancers--role of estrogen receptor and HER2 reactivation.Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(6):R121. doi: 10.1186/bcr3067. Epub 2011 Nov 28. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22123186 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of mucin4 in ER-positive/HER2-overexpressing breast cancer xenografts with acquired resistance to endocrine and HER2-targeted therapies.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Jul;134(2):583-93. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2082-9. Epub 2012 May 29. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 22644656 Free PMC article.
-
Lapatinib restores hormone sensitivity with differential effects on estrogen receptor signaling in cell models of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer with acquired endocrine resistance.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Mar 1;16(5):1486-97. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1764. Epub 2010 Feb 23. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20179226
-
De-escalation of treatment in HER2-positive breast cancer: Determinants of response and mechanisms of resistance.Breast. 2017 Aug;34 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S19-S26. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2017.06.022. Epub 2017 Jul 4. Breast. 2017. PMID: 28687441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does lapatinib work against HER2-negative breast cancers?Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Mar 1;16(5):1355-7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3223. Epub 2010 Feb 23. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20179241 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of New Mono/Dihydroxynaphthoquinone as Lead Agents That Inhibit the Growth of Refractive and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Lines.ACS Omega. 2019 Jun 19;4(6):10610-10619. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b00929. eCollection 2019 Jun 30. ACS Omega. 2019. PMID: 31460159 Free PMC article.
-
3D Visualization of the Dynamic Bidirectional Talk Between ER/PR and Her2 Pathways.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:15330338211065603. doi: 10.1177/15330338211065603. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34898327 Free PMC article.
-
Application of the CRISPR/Cas9 System to Drug Resistance in Breast Cancer.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018 Apr 15;5(6):1700964. doi: 10.1002/advs.201700964. eCollection 2018 Jun. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018. PMID: 29938175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Treatment and Resistance.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1464:495-525. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-70875-6_24. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39821040 Review.
-
HER2 genomic amplification in circulating tumor DNA and estrogen receptor positivity predict primary resistance to trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2018 Sep;25(5):605-613. doi: 10.1007/s12282-018-0861-9. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Breast Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29700710 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Citri A, Yarden Y. EGF-ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2006;7(7):505–16. Epub 2006/07/11. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987;235(4785):177–82. Epub 1987/01/09. - PubMed
-
- Seshadri R, Firgaira FA, Horsfall DJ, McCaul K, Setlur V, Kitchen P. Clinical significance of HER-2/neu oncogene amplification in primary breast cancer. The South Australian Breast Cancer Study Group. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 1993;11(10):1936–42. Epub 1993/10/01. - PubMed
-
- Tortora G. Mechanisms of resistance to HER2 target therapy. Journal of the National Cancer Institute Monographs. 2011;2011(43):95–8. Epub 2011/11/02. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

