Flow-diverter stenting in post-traumatic pseudoaneurysm of cavernous internal carotid artery with epistaxis
- PMID: 26015524
- PMCID: PMC4757263
- DOI: 10.1177/1591019915582154
Flow-diverter stenting in post-traumatic pseudoaneurysm of cavernous internal carotid artery with epistaxis
Abstract
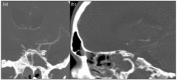
This paper is a case report of a young patient after a major head trauma causing multiple skull base fractures. The trauma occasioned pseudoaneurysm (PSA) from intracavernous C4 segment of left internal carotid artery (ICA) protruding in the sphenoidal sinus. After two months, two episodes of massive epistaxis occurred. Consequently, the post-traumatic PSA was treated, after carotid occlusion test, with flow-diverter stent positioning. A computed tomography angiography study performed in the following days showed complete resolution of the post-traumatic PSA lesion and ICA patency.
Keywords: Flow-diverter stenting; internal carotid artery; post-traumatic pseudoaneurysm.
© The Author(s) 2015.
Figures



References
-
- Chen D, Concus AP, Halbach BV, et al. Epistaxis originating from traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the internal carotid artery: diagnosis and endovascular therapy. Laryngoscope 1998; 108: 326–331. - PubMed
-
- Asma A, Primuharsa Putra S, Saim L. Massive epistaxis secondary to pseudoaneurysm of internal carotid artery. Med J Malesia 2006; 61: 84–87. - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Li J, Xu G, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of traumatic internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm primarily manifested by repeated epistaxis. Turkish Neurosurg 2013; 23: 716–720. - PubMed
-
- Goleas J, Mikhael MA, Paige ML, et al. Intracavernous carotid artery aneurysm presenting as recurrent epistaxis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1991; 100: 577–579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

