Human HLA-G+ extravillous trophoblasts: Immune-activating cells that interact with decidual leukocytes
- PMID: 26015573
- PMCID: PMC4466754
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1507977112
Human HLA-G+ extravillous trophoblasts: Immune-activating cells that interact with decidual leukocytes
Abstract
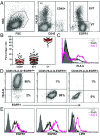
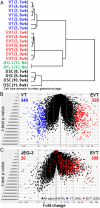
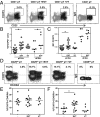
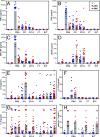
Invading human leukocyte antigen-G+ (HLA-G+) extravillous trophoblasts (EVT) are rare cells that are believed to play a key role in the prevention of a maternal immune attack on foreign fetal tissues. Here highly purified HLA-G+ EVT and HLA-G- villous trophoblasts (VT) were isolated. Culture on fibronectin that EVT encounter on invading the uterus increased HLA-G, EGF-Receptor-2, and LIF-Receptor expression on EVT, presumably representing a further differentiation state. Microarray and functional gene set enrichment analysis revealed a striking immune-activating potential for EVT that was absent in VT. Cocultures of HLA-G+ EVT with sample matched decidual natural killer cells (dNK), macrophages, and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were established. Interaction of EVT with CD4+ T cells resulted in increased numbers of CD4+CD25(HI)FOXP3+CD45RA+ resting regulatory T cells (Treg) and increased the expression level of the Treg-specific transcription factor FOXP3 in these cells. However, EVT did not enhance cytokine secretion in dNK, whereas stimulation of dNK with mitogens or classical natural killer targets confirmed the distinct cytokine secretion profiles of dNK and peripheral blood NK cells (pNK). EVT are specialized cells involved in maternal-fetal tolerance, the properties of which are not imitated by HLA-G-expressing surrogate cell lines.
Keywords: FOXP3; NK cell; Treg; human; pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: J.L.S. is a consultant for King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
Figures
References
-
- Moffett A, Loke C. Immunology of placentation in eutherian mammals. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(8):584–594. - PubMed
-
- Jokhi PP, King A, Loke YW. Reciprocal expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) and c-erbB2 by non-invasive and invasive human trophoblast populations. Cytokine. 1994;6(4):433–442. - PubMed
-
- Kimber SJ. Leukaemia inhibitory factor in implantation and uterine biology. Reproduction. 2005;130(2):131–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

