Staphylococcus aureus infections: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management
- PMID: 26016486
- PMCID: PMC4451395
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00134-14
Staphylococcus aureus infections: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management
Abstract
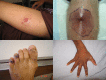
Staphylococcus aureus is a major human pathogen that causes a wide range of clinical infections. It is a leading cause of bacteremia and infective endocarditis as well as osteoarticular, skin and soft tissue, pleuropulmonary, and device-related infections. This review comprehensively covers the epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management of each of these clinical entities. The past 2 decades have witnessed two clear shifts in the epidemiology of S. aureus infections: first, a growing number of health care-associated infections, particularly seen in infective endocarditis and prosthetic device infections, and second, an epidemic of community-associated skin and soft tissue infections driven by strains with certain virulence factors and resistance to β-lactam antibiotics. In reviewing the literature to support management strategies for these clinical manifestations, we also highlight the paucity of high-quality evidence for many key clinical questions.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous