MicroRNA-217 functions as a prognosis predictor and inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and invasion via an AEG-1 dependent mechanism
- PMID: 26016795
- PMCID: PMC4446846
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-1438-z
MicroRNA-217 functions as a prognosis predictor and inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and invasion via an AEG-1 dependent mechanism
Abstract
Background: Recent studies have indicated the possible function of miR-217 in tumorigenesis. However, the roles of miR-217 in colorectal cancer (CRC) are still largely unknown.
Methods: We examined the expression of miR-217 and AEG-1 in 50 CRC tissues and the corresponding noncancerous tissues by qRT-PCR. The clinical significance of miR-217 was analyzed. CRC cell lines with miR-217 upregulation and AEG-1 silencing were established and the effects on tumor growth in vitro and in vivo were assessed. Dual-luciferase reporter gene assays were also performed to investigate the interaction between miR-217 and AEG-1.
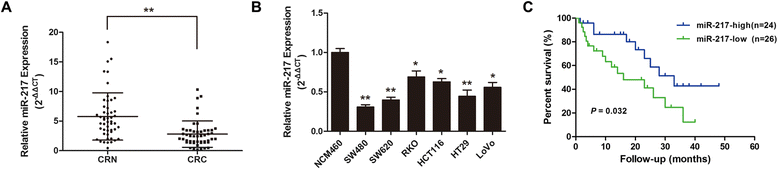
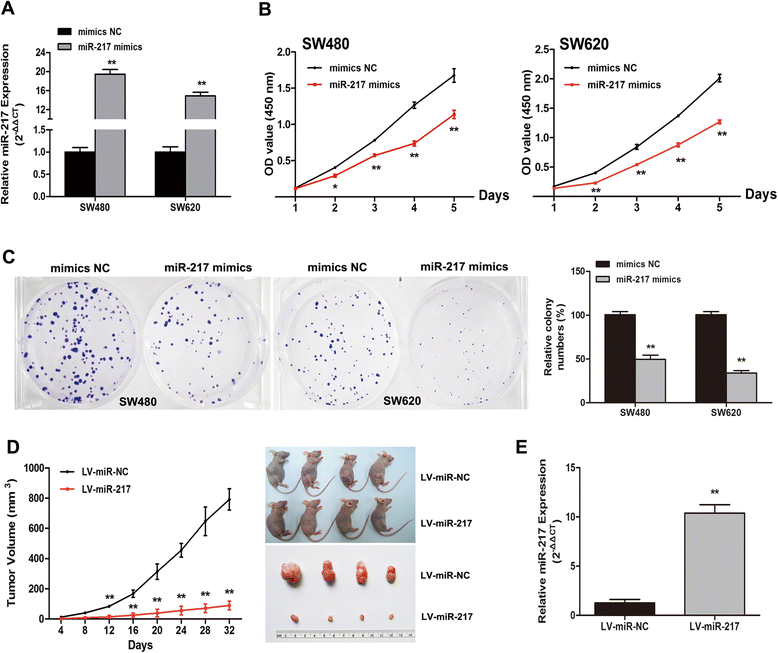
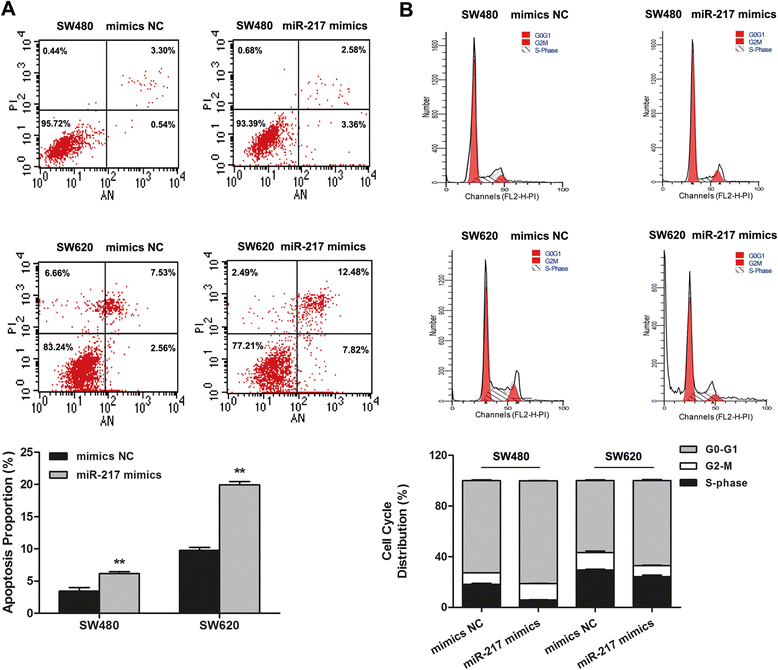
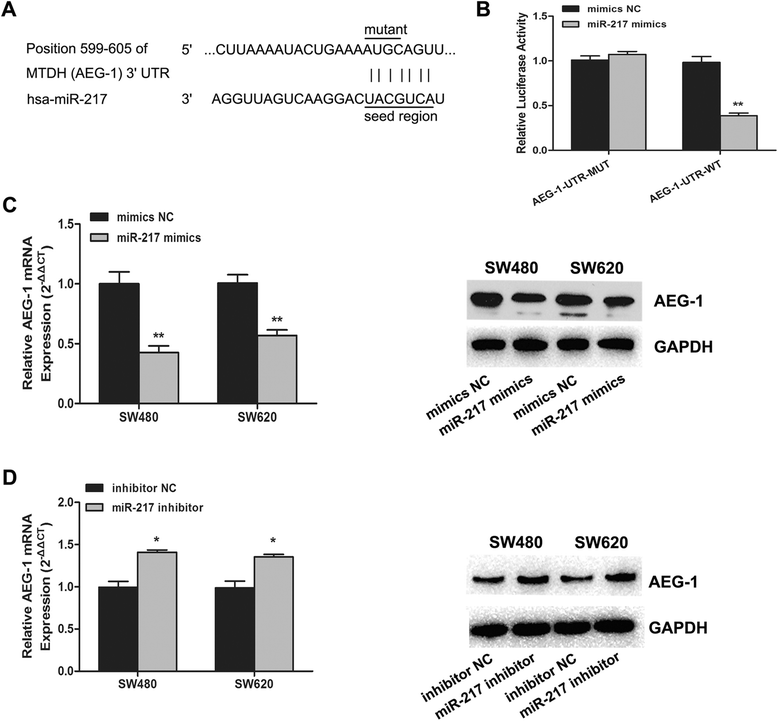
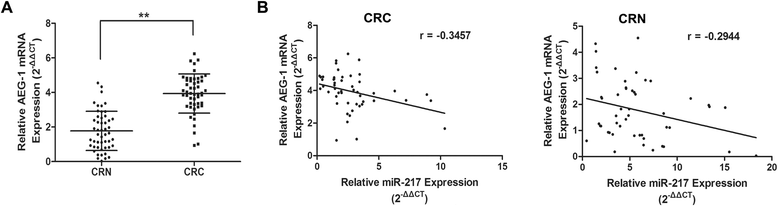
Results: Our data demonstrated that miR-217 was significantly downregulated in 50 pairs of colorectal cancer tissues. MiR-217 expression levels were closely correlated with tumor differentiation. Moreover, decreased miR-217 expression was also associated with shorter overall survival of CRC patients. MiR-217 overexpression significantly inhibited proliferation, colony formation and invasiveness of CRC cells by promoting apoptosis and G0/G1 phase arrest. Interestingly, ectopic miR-217 expression decreased AEG-1 expression and repressed luciferase reporter activity associated with the AEG-1 3'-untranslated region (UTR). AEG-1 silencing resulted in similar biological behavior changes to those associated with miR-217 overexpression. Finally, in a nude mouse xenografted tumor model, miR-217 overexpression significantly suppressed CRC cell growth.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that miR-217 has considerable value as a prognostic marker and potential therapeutic target in CRC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo.Oncogene. 2012 Jul 12;31(28):3357-69. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.500. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22056881
-
microRNA-7 is a novel inhibitor of YY1 contributing to colorectal tumorigenesis.Oncogene. 2013 Oct 17;32(42):5078-88. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.526. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 23208495
-
Long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 sponges miR-194 to promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via up-regulating TGFα.Cancer Biomark. 2018;23(1):145-156. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181503. Cancer Biomark. 2018. PMID: 30010111
-
MicroRNAs: Potential candidates for diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Feb;233(2):901-913. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25801. Epub 2017 May 15. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28092102 Review.
-
The emerging role of miR-375 in cancer.Int J Cancer. 2014 Sep 1;135(5):1011-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28563. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24166096 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-217 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by targeting Runx2 in human glioma.Am J Transl Res. 2016 Mar 15;8(3):1482-91. eCollection 2016. Am J Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 27186274 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of microRNAs in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Apr 30;10:907-929. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S157493. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 29750053 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation by targeting tumor suppressor TET1 in colorectal cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Mar 1;11(3):1439-1445. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31938241 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-Mediated Transfer of circ_0000338 Enhances 5-Fluorouracil Resistance in Colorectal Cancer through Regulating MicroRNA 217 (miR-217) and miR-485-3p.Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Apr 22;41(5):e00517-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00517-20. Print 2021 Apr 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33722958 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA HOXD-AS1 promotes tumor progression and predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer.Int J Oncol. 2018 Jul;53(1):21-32. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4400. Epub 2018 May 9. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29749477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pichler M, Ress AL, Winter E, Stiegelbauer V, Karbiener M, Schwarzenbacher D, et al. MiR-200a regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition-related gene expression and determines prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2014;110(6):1614–21. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.51. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

