Environmental Enrichment Reduces Anxiety by Differentially Activating Serotonergic and Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-Ergic System in Indian Field Mouse (Mus booduga): An Animal Model of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
- PMID: 26016844
- PMCID: PMC4446351
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127945
Environmental Enrichment Reduces Anxiety by Differentially Activating Serotonergic and Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-Ergic System in Indian Field Mouse (Mus booduga): An Animal Model of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Abstract
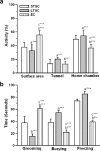
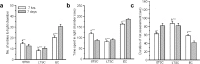
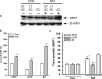
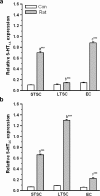
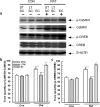
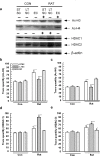
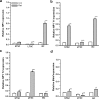
Exposure to a predator elicits an innate fear response and mimics several behavioral disorders related to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The protective role of an enriched condition (EC) against psychogenic stressors in various animal models has been well documented. However, this condition has not been tested in field mice in the context of PTSD. In this study, we show that field mice (Mus booduga) housed under EC exhibit predominantly proactive and less reactive behavior compared with mice housed under standard conditions (SC) during exposure to their natural predator (field rat Rattus rattus). Furthermore, we observed that EC mice displayed less anxiety-like behavior in an elevated plus maze (EPM) and light/dark-box after exposure to the predator (7 hrs/7 days). In EC mice, predator exposure elevated the level of serotonin (5-Hydroxytrypamine, [5-HT]) in the amygdala as part of the coping response. Subsequently, the serotonin transporter (SERT) and 5-HT1A receptor were up-regulated significantly, but the same did not occur in the 5-HT2C receptor, which is associated with the activation of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase-II (CaMKII) and a transcription factor cAMP response element binding protein (CREB). Our results show that predator exposure induced the activation of CaMKII/CREB, which is accompanied with increased levels of histone acetylation (H3, H4) and decreased histone deacetylases (HDAC1, 2). Subsequently, in the amygdala, the transcription of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neuropeptide Y (NPY) and its Y1 receptor were up-regulated, whereas the Y2 receptor was down-regulated. Therefore, EC facilitated a coping response against a fear associated cue in a PTSD animal model and reduced anxiety by differentially activating serotonergic and NPY-ergic systems.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Adamec R, Kent P, Anisman H, Shallow, Merali Z (1998) Neural plasticity, neuropeptides and anxiety in animals: implications for understanding and treating affective disorder following traumatic stress in humans. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23: 301–318. - PubMed
-
- Adamec RE, Blundell J, Burton P (2005) Neural circuit changes mediating lasting brain and behavioral response to predator stress. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:1225–1241. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi LK, Nakashima BR, Hong H, Watanabe K (2005) The smell of danger: a behavioral and neural analysis of predator odor-induced fear. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:1157–1167. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi LK, Hubbard DT, Lee I, Dar Y, Sipes SM (2007) Predator odor-induced conditioned fear involves the basolateral and medial amygdala. Behav Neurosci 121:100–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

