DNA-PKcs plays role in cancer metastasis through regulation of secreted proteins involved in migration and invasion
- PMID: 26017556
- PMCID: PMC4614356
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1026522
DNA-PKcs plays role in cancer metastasis through regulation of secreted proteins involved in migration and invasion
Abstract
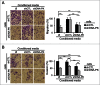
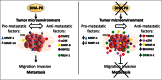
The DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) plays a major role in DNA damage signaling and repair and is also frequently overexpressed in tumor metastasis. We used isogenic cell lines expressing different levels of DNA-PKcs to investigate the role of DNA-PKcs in metastatic development. We found that DNA-PKcs participates in melanoma primary tumor and metastasis development by stimulating angiogenesis, migration and invasion. Comparison of conditioned medium content from DNA-PKcs-proficient and deficient cells reveals that DNA-PKcs controls secretion of at least 103 proteins (including 44 metastasis-associated with FBLN1, SERPINA3, MMP-8, HSPG2 and the inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases, such as α-2M and TIMP-2). High throughput analysis of secretomes, proteomes and transcriptomes, indicate that DNA-PKcs regulates the secretion of 85 proteins without affecting their gene expression. Our data demonstrate that DNA-PKcs has a pro-metastatic activity via the modification of the tumor microenvironment. This study shows for the first time a direct link between DNA damage repair and cancer metastasis and highlights the importance of DNA-PKcs as a potential target for anti-metastatic treatment.
Keywords: CM, conditioned media; DNA damage; DNA-PK; DNA-PK, DNA-dependent protein kinase; DNA-PKcs, DNA-PK catalytic subunit; DSB, double-strand break; ECM, extracellular matrix; MMP inhibition; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MS, mass spectrometry; NHEJ, non-homologous end joining; SILAC, stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase.; metastasis; secretion; α-2M, α-2-macroglobulin.
Figures





References
-
- Ong SE, Blagoev B, Kratchmarova I, Kristensen DB, Steen H, Pandey A, Mann M. Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture, SILAC, as a simple and accurate approach to expression proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics 2002; 1:376-86; PMID:12118079; http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M200025-MCP200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shintani S, Mihara M, Li C, Nakahara Y, Hino S, Nakashiro K, Hamakawa H. Up-regulation of DNA-dependent protein kinase correlates with radiation resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci 2003; 94:894-900; PMID:14556663; http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01372.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Helleday T, Petermann E, Lundin C, Hodgson B, Sharma RA. DNA repair pathways as targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8:193-204; PMID:18256616; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrc2342 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lieberman HB. DNA damage repair and response proteins as targets for cancer therapy. Curr Med Chem 2008; 15:360-7; PMID:18288990; http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/092986708783497328 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mao Z, Bozzella M, Seluanov A, Gorbunova V. Comparison of nonhomologous end joining and homologous recombination in human cells. DNA Repair 2008; 7:1765-71; PMID:18675941; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.06.018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
