Involvement of the Rac1-IRSp53-Wave2-Arp2/3 Signaling Pathway in HIV-1 Gag Particle Release in CD4 T Cells
- PMID: 26018170
- PMCID: PMC4524266
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00469-15
Involvement of the Rac1-IRSp53-Wave2-Arp2/3 Signaling Pathway in HIV-1 Gag Particle Release in CD4 T Cells
Abstract
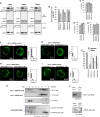
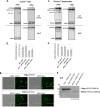
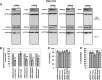
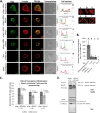
During HIV-1 assembly, the Gag viral proteins are targeted and assemble at the inner leaflet of the cell plasma membrane. This process could modulate the cortical actin cytoskeleton, located underneath the plasma membrane, since actin dynamics are able to promote localized membrane reorganization. In addition, activated small Rho GTPases are known for regulating actin dynamics and membrane remodeling. Therefore, the modulation of such Rho GTPase activity and of F-actin by the Gag protein during virus particle formation was considered. Here, we studied the implication of the main Rac1, Cdc42, and RhoA small GTPases, and some of their effectors, in this process. The effect of small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated Rho GTPases and silencing of their effectors on Gag localization, Gag membrane attachment, and virus-like particle production was analyzed by immunofluorescence coupled to confocal microscopy, membrane flotation assays, and immunoblot assays, respectively. In parallel, the effect of Gag expression on the Rac1 activation level was monitored by G-LISA, and the intracellular F-actin content in T cells was monitored by flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy. Our results revealed the involvement of activated Rac1 and of the IRSp53-Wave2-Arp2/3 signaling pathway in HIV-1 Gag membrane localization and particle release in T cells as well as a role for actin branching and polymerization, and this was solely dependent on the Gag viral protein. In conclusion, our results highlight a new role for the Rac1-IRSp53-Wave2-Arp2/3 signaling pathway in the late steps of HIV-1 replication in CD4 T lymphocytes.
Importance: During HIV-1 assembly, the Gag proteins are targeted and assembled at the inner leaflet of the host cell plasma membrane. Gag interacts with specific membrane phospholipids that can also modulate the regulation of cortical actin cytoskeleton dynamics. Actin dynamics can promote localized membrane reorganization and thus can be involved in facilitating Gag assembly and particle formation. Activated small Rho GTPases and effectors are regulators of actin dynamics and membrane remodeling. We thus studied the effects of the Rac1, Cdc42, and RhoA GTPases and their specific effectors on HIV-1 Gag membrane localization and viral particle release in T cells. Our results show that activated Rac1 and the IRSp53-Wave2-Arp2/3 signaling pathway are involved in Gag plasma membrane localization and viral particle production. This work uncovers a role for cortical actin through the activation of Rac1 and the IRSp53/Wave2 signaling pathway in HIV-1 particle formation in CD4 T lymphocytes.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
HIV-1 triggers WAVE2 phosphorylation in primary CD4 T cells and macrophages, mediating Arp2/3-dependent nuclear migration.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 7;289(10):6949-6959. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.492132. Epub 2014 Jan 10. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24415754 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane targeting of WAVE2 is not sufficient for WAVE2-dependent actin polymerization: a role for IRSp53 in mediating the interaction between Rac and WAVE2.J Cell Sci. 2008 Feb 1;121(Pt 3):379-90. doi: 10.1242/jcs.010272. Epub 2008 Jan 15. J Cell Sci. 2008. PMID: 18198193 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of WAVE2 complex-induced actin polymerization by membrane-bound IRSp53, PIP(3), and Rac.J Cell Biol. 2006 May 22;173(4):571-85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200509067. Epub 2006 May 15. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16702231 Free PMC article.
-
A role for the small GTPase Rac1 in vaccinia actin-based motility.Small GTPases. 2015;6(2):119-22. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2015.1055182. Small GTPases. 2015. PMID: 26147090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and role of WASP and WAVE in Rho GTPase signalling in cancer.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2014 May-Jun;11(3):155-65. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24969695 Review.
Cited by
-
Various Facets of Pathogenic Lipids in Infectious Diseases: Exploring Virulent Lipid-Host Interactome and Their Druggability.J Membr Biol. 2020 Oct;253(5):399-423. doi: 10.1007/s00232-020-00135-0. Epub 2020 Aug 24. J Membr Biol. 2020. PMID: 32833058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV-1 Mediated Cortical Actin Disruption Mirrors ARP2/3 Defects Found in Primary T Cell Immunodeficiencies.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 15:2023.07.27.550856. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.27.550856. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38405733 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Distinct chikungunya virus polymerase palm subdomains contribute to virus replication and virion assembly.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 15:2024.01.15.575630. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.15.575630. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: PLoS Pathog. 2024 Oct 14;20(10):e1011972. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011972. PMID: 38293111 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
CD28 and chemokine receptors: Signalling amplifiers at the immunological synapse.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 2;13:938004. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.938004. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35983040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV-1 diverts cortical actin for particle assembly and release.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 31;14(1):6945. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41940-0. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37907528 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

