High-flow carotid cavernous fistula and the use of a microvascular plug system: initial experience
- PMID: 26019711
- PMCID: PMC4439797
- DOI: 10.1159/000369477
High-flow carotid cavernous fistula and the use of a microvascular plug system: initial experience
Abstract
Purpose: We report our initial experience using a detachable microvascular plug system to occlude the internal carotid artery during endovascular treatment of high-flow carotid cavernous fistula.
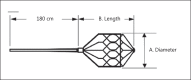
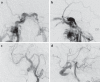
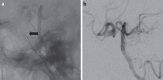
Case and technique: An 87-year-old patient was admitted for acute-onset double vision with associated right-eye ptosis. Exam revealed a pupil-sparing, partial right third cranial nerve palsy. MRI showed a carotid cavernous fistula with high-flow drainage. Digital subtraction angiography showed a high-flow, right-sided, direct carotid cavernous fistula with flow from the proximal right internal carotid artery. The ophthalmic artery, posterior communicating artery and anterior communicating arteries supplied retrograde flow to the fistula through the internal carotid artery. Obliteration of the fistula was achieved through coil embolization in combination with proximal and distal microvascular plugs (Reverse Medical, Irvine, Calif., USA).
Conclusion: The microvascular plug is a new addition to current endovascular embolization devices for the treatment of high-flow, direct carotid cavernous fistulas. This technique offers easy navigability through tortuous arteries, precise localization and immediate occlusion, which may allow shorter procedure and fluoroscopy times and increased cost-effectiveness. Larger case series are needed to support our observation.
Keywords: Carotid cavernous fistula; High flow; Microvascular plug.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endovascular treatment of a direct post-traumatic carotid-cavernous fistula with electrolytically detachable coils.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2006;118 Suppl 2:80-4. doi: 10.1007/s00508-006-0541-1. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2006. PMID: 16817051
-
Transvenous embolization of dural carotid cavernous fistula through the facial and ophthalmic vein.Vojnosanit Pregl. 2011 Dec;68(12):1079-83. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2011. PMID: 22352273
-
Atypical Manifestation of Direct Low-Flow Carotid-Cavernous Fistula: Case Report and Review of the Literature.World Neurosurg. 2019 May;125:456-460. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.02.027. Epub 2019 Feb 26. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 30818073 Review.
-
A Lesson Learnt from a Dural Carotid Cavernous Fistula-induced Superior Ophthalmic Vein Occlusion with Posterior Ischaemic Optic Neuropathy.Neuroophthalmology. 2021 Nov 11;46(3):199-202. doi: 10.1080/01658107.2021.2000622. eCollection 2022. Neuroophthalmology. 2021. PMID: 35574167 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous carotid-cavernous fistula supplied by the contralateral meningohypophyseal trunk: case report and literature review.J Neurosurg Sci. 2010 Mar;54(1):45-8. J Neurosurg Sci. 2010. PMID: 20436398 Review.
Cited by
-
MVP (Micro Vascular Plug®) embolization of severe renal hemorrhages after nephrostomic tube placement.CVIR Endovasc. 2019 Dec 30;2(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s42155-019-0087-8. CVIR Endovasc. 2019. PMID: 32026228 Free PMC article.
-
Direct carotid cavernous sinus fistulae: vessel reconstruction using flow-diverting implants.Clin Neuroradiol. 2017 Dec;27(4):493-501. doi: 10.1007/s00062-016-0511-6. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Clin Neuroradiol. 2017. PMID: 27129454 Free PMC article.
-
Use of the Hourglass peripheral embolisation device: early experiences.Eur Radiol Exp. 2018;2(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s41747-017-0035-0. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Eur Radiol Exp. 2018. PMID: 29708191 Free PMC article.
-
Embolization with MVP (Micro Vascular Plug®): experience on 104 patients in emergent and elective scenarios.CVIR Endovasc. 2021 Jul 12;4(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s42155-021-00246-2. CVIR Endovasc. 2021. PMID: 34250548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yanoff M, Duker JS. St. Louis: Mosby; 2004. Ophthalmology, ed 2.
-
- Nocini P, et al. Cavernous sinus-carotid fistula: a complication of maxillofacial injury. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1995;24:276–278. - PubMed
-
- Neil MR. Carotid-cavernous fistulas. Walsh and Hoyt's Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Chapter 42. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2005:2263–2296.
-
- Das JK, et al. Clinical spectrum of spontaneous carotid-cavernous fistula. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2007;55:310–312. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

