New prognostic markers in liver cirrhosis
- PMID: 26019739
- PMCID: PMC4438498
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i9.1244
New prognostic markers in liver cirrhosis
Abstract
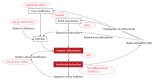
Determining the prognosis of cirrhotic patients is not an easy task. Prognostic scores, like Child-Pugh and Model of End-stage Liver Disease scores, are commonly used by hepatologists, but do not always reflect superimposed events that may strongly influence the prognosis. Among them, bacterial intestinal translocation is a key phenomenon for the development of cirrhosis-related complications. Several biological variables (C-reactive protein, serum free cortisol, copeptin, von Willebrand factor antigen) are surrogates of "inflammatory stress" and have recently been identified as potential prognostic markers in cirrhotic patients. Most of these above mentioned markers were investigated in pilot studies with sometimes a modest sample size but allow us to catch a glimpse of the pathophysiological mechanisms leading to the worsening of cirrhosis. These new data should generate further well-designed studies to better assess the benefit for liver function of preventing intestinal bacterial translocation and microvascular thrombosis. The control of infection is vital and among all actors of immunity, vitamin D also appears to act as an anti-infective agent and therefore has probably a prognostic value.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; Cirrhosis; Copeptin; Serum free cortisol; Vitamin D; Von Willebrand factor antigen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of von-Willebrand factor in patients with liver cirrhosis and its relation to other prognostic indicators.World J Hepatol. 2022 Apr 27;14(4):812-826. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i4.812. World J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35646274 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma copeptin, a possible prognostic marker in cirrhosis.Liver Int. 2013 Jul;33(6):843-51. doi: 10.1111/liv.12175. Epub 2013 Apr 7. Liver Int. 2013. PMID: 23560938
-
Copeptin is an independent prognostic factor for transplant-free survival in cirrhosis.Liver Int. 2016 Apr;36(4):530-7. doi: 10.1111/liv.12992. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Liver Int. 2016. PMID: 26502363
-
Vitamin D deficiency in patients with liver cirrhosis.Ann Gastroenterol. 2016 Jul-Sep;29(3):297-306. doi: 10.20524/aog.2016.0037. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Ann Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27366029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluid Biomarkers for Predicting the Prognosis of Liver Cirrhosis.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Mar 20;2020:7170457. doi: 10.1155/2020/7170457. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32280697 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cohort Profile: Shiraz Pediatric Liver Cirrhosis Cohort (SPLCCS).Arch Iran Med. 2023 Apr 1;26(4):229-233. doi: 10.34172/aim.2023.35. Arch Iran Med. 2023. PMID: 38301084 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio with Child-Pugh and PELD/MELD scores to predict the outcome of children with cirrhosis.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2021 Dec;7(4):351-357. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2021.111419. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 35402724 Free PMC article.
-
CRP and the Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis.Maedica (Bucur). 2021 Sep;16(3):353-361. doi: 10.26574/maedica.2021.16.3.353. Maedica (Bucur). 2021. PMID: 34925587 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of von-Willebrand factor in patients with liver cirrhosis and its relation to other prognostic indicators.World J Hepatol. 2022 Apr 27;14(4):812-826. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i4.812. World J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35646274 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 as prognostic biomarker in liver cirrhosis.World J Hepatol. 2016 Jun 18;8(17):739-48. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i17.739. World J Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27330683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levesque E, Hoti E, Azoulay D, Ichaï P, Habouchi H, Castaing D, Samuel D, Saliba F. Prospective evaluation of the prognostic scores for cirrhotic patients admitted to an intensive care unit. J Hepatol. 2012;56:95–102. - PubMed
-
- Bota DP, Van Nuffelen M, Zakariah AN, Vincent JL. Serum levels of C-reactive protein and procalcitonin in critically ill patients with cirrhosis of the liver. J Lab Clin Med. 2005;146:347–351. - PubMed
-
- Park WB, Lee KD, Lee CS, Jang HC, Kim HB, Lee HS, Oh MD, Choe KW. Production of C-reactive protein in Escherichia coli-infected patients with liver dysfunction due to liver cirrhosis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005;51:227–230. - PubMed
-
- Devaraj S, Kumaresan PR, Jialal I. C-reactive protein induces release of both endothelial microparticles and circulating endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo: further evidence of endothelial dysfunction. Clin Chem. 2011;57:1757–1761. - PubMed
-
- Thabut D, Massard J, Gangloff A, Carbonell N, Francoz C, Nguyen-Khac E, Duhamel C, Lebrec D, Poynard T, Moreau R. Model for end-stage liver disease score and systemic inflammatory response are major prognostic factors in patients with cirrhosis and acute functional renal failure. Hepatology. 2007;46:1872–1882. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

