Emphysematous pyelonephritis: Time for a management plan with an evidence-based approach
- PMID: 26019934
- PMCID: PMC4434438
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aju.2013.09.005
Emphysematous pyelonephritis: Time for a management plan with an evidence-based approach
Abstract
Introduction: Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is a life-threatening necrotising kidney infection, but there is no consensus on the best management.
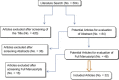
Methods: We systematically reviewed previous articles published from 1980 to 2013 that included studies reporting on EPN, and applying the Cochrane guidelines, we conducted a meta-analysis of the results.
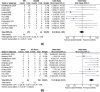
Results: In all, 32 studies were included, with results for 628 patients (mean age 56.6 years, range 33.8-79.9). There were 462 women, outnumbering men by 3:1. Diabetes was present in 85% of the cases. Fevers and rigor (74.7%), pyuria (78.2%) and pain (70.4%) were the most common symptoms. Shock was associated with 54.4% of deaths while obstructive uropathy was associated with 15.1% of deaths. Computed tomography was diagnostic in all the cases. Percutaneous drainage (PCD) and medical management (MM) alone were associated with a significantly lower mortality rate than was emergency nephrectomy (EN), with an odds ratio (95% confidence interval) for PCD vs. EN of 3.13 (1.89-5.16; P < 0.001), for EN vs. MM of 2.84 (1.62-4.99; P = 0.001), and of 0.91 (0.53-1.56; P = 0.73, i.e., no difference) for PCD vs. MM. Open drainage also had a significantly lower mortality rate than EN, with a ratio of 0.12 (0.02-0.91; P < 0.04).
Conclusion: The overall mortality rate was ≈18%; shock was associated with a high mortality rate and therefore should be managed aggressively. PCD and MM were associated with significantly higher survival rates than EN, and therefore EN should only be considered if the patient does not improve despite other treatments.
Keywords: DM, diabetes mellitus; EN, nephrectomy; EPN, emphysematous pyelonephritis; Emergency nephrectomy; Emphysematous pyelonephritis; Infection; MM, medical management; OD, open drainage; OR, odds ratio; PCD, percutaneous drainage; Percutaneous drainage; Pyelonephritis.
Figures




References
-
- Narlawar R.S., Raut A.A., Nagar A., Hira P., Hanchate V., Asrani A. Imaging features and guided drainage in emphysematous pyelonephritis: a study of 11 cases. Clin Radiol. 2004;59:192–197. - PubMed
-
- Shokeir A.A., El-Azab M., Mohsen T., El-Diasty T. Emphysematous pyelonephritis: a 15-year experience with 20 cases. Urology. 1997;49:343–346. - PubMed
-
- Tang H.J., Li C.M., Yen M.Y., Chen Y.S., Wann S.R., Lin H.H. Clinical characteristics of emphysematous pyelonephritis. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2001;34:125–130. - PubMed
-
- Wan Y.L., Lee T.Y., Bullard M.J., Tsai C.C. Acute gas-producing bacterial renal infection. correlation between imaging findings and clinical outcome. Radiology. 1996;198:433–438. - PubMed
-
- Somani B.K., Nabi G., Thorpe P., Hussey J., Cook J., N’Dow J. Is percutaneous drainage the new gold standard in the management of emphysematous pyelonephritis? Evidence from a systematic review. J Urol. 2008;179:1844–1849. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
