Auxin-Mediated Transcriptional System with a Minimal Set of Components Is Critical for Morphogenesis through the Life Cycle in Marchantia polymorpha
- PMID: 26020919
- PMCID: PMC4447296
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005084
Auxin-Mediated Transcriptional System with a Minimal Set of Components Is Critical for Morphogenesis through the Life Cycle in Marchantia polymorpha
Erratum in
-
Correction: Auxin-Mediated Transcriptional System with a Minimal Set of Components Is Critical for Morphogenesis through the Life Cycle in Marchantia polymorpha.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jun 26;11(6):e1005365. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005365. eCollection 2015 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26115224 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
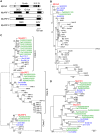
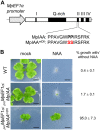
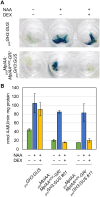
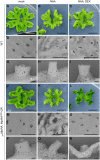
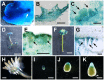
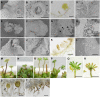
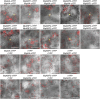
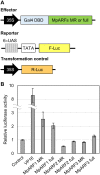
The plant hormone auxin regulates many aspects of plant growth and development. Recent progress in Arabidopsis provided a scheme that auxin receptors, TIR1/AFBs, target transcriptional co-repressors, AUX/IAAs, for degradation, allowing ARFs to regulate transcription of auxin responsive genes. The mechanism of auxin-mediated transcriptional regulation is considered to have evolved around the time plants adapted to land. However, little is known about the role of auxin-mediated transcription in basal land plant lineages. We focused on the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha, which belongs to the earliest diverging lineage of land plants. M. polymorpha has only a single TIR1/AFB (MpTIR1), a single AUX/IAA (MpIAA), and three ARFs (MpARF1, MpARF2, and MpARF3) in the genome. Expression of a dominant allele of MpIAA with mutations in its putative degron sequence conferred an auxin resistant phenotype and repressed auxin-dependent expression of the auxin response reporter proGH3:GUS. We next established a system for DEX-inducible auxin-response repression by expressing the putatively stabilized MpIAA protein fused with the glucocorticoid receptor domain (MpIAA(mDII)-GR). Repression of auxin responses in (pro)MpIAA:MpIAA(mDII)-GR plants caused severe defects in various developmental processes, including gemmaling development, dorsiventrality, organogenesis, and tropic responses. Transient transactivation assays showed that the three MpARFs had different transcriptional activities, each corresponding to their phylogenetic classifications. Moreover, MpIAA and MpARF proteins interacted with each other with different affinities. This study provides evidence that pleiotropic auxin responses can be achieved by a minimal set of auxin signaling factors and suggests that the transcriptional regulation mediated by TIR1/AFB, AUX/IAA, and three types of ARFs might have been a key invention to establish body plans of land plants. We propose that M. polymorpha is a good model to investigate the principles and the evolution of auxin-mediated transcriptional regulation and its roles in land plant morphogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Friml J, Vieten A, Sauer M, Weijers D, Schwarz H, et al. (2003) Efflux-dependent auxin gradients establish the apical-basal axis of Arabidopsis. Nature 426: 147–153. - PubMed
-
- Benkova E, Michniewicz M, Sauer M, Teichmann T, Seifertova D, et al. (2003) Local, efflux-dependent auxin gradients as a common module for plant organ formation. Cell 115: 591–602. - PubMed
-
- Tatematsu K, Kumagai S, Muto H, Sato A, Watahiki MK, et al. (2004) MASSUGU2 encodes Aux/IAA19, an auxin-regulated protein that functions together with the transcriptional activator NPH4/ARF7 to regulate differential growth responses of hypocotyl and formation of lateral roots in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 16: 379–393. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

