RLIP76 Targeted Therapy for Kidney Cancer
- PMID: 26021465
- PMCID: PMC5384263
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-015-1723-1
RLIP76 Targeted Therapy for Kidney Cancer
Abstract
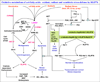
Despite recent improvements in chemotherapeutic approaches to treating kidney cancer, this malignancy remains deadly if not found and removed at an early stage of the disease. Kidney cancer is highly drug-resistant, which may at least partially result from high expression of transporter proteins in the cell membranes of kidney cells. Although these transporter proteins can contribute to drug-resistance, targeting proteins from the ATP-binding cassette transporter family has not been effective in reversing drug-resistance in kidney cancer. Recent studies have identified RLIP76 as a key stress-defense protein that protects normal cells from damage caused by stress conditions, including heat, ultra-violet light, X-irradiation, and oxidant/electrophilic toxic chemicals, and is crucial for protecting cancer cells from apoptosis. RLIP76 is the predominant glutathione-electrophile-conjugate (GS-E) transporter in cells, and inhibiting it with antibodies or through siRNA or antisense causes apoptosis in many cancer cell types. To date, blocking of RLIP76, either alone or in combination with chemotherapeutic drugs, as a therapeutic strategy for kidney cancer has not yet been evaluated in human clinical trials, although there is considerable potential for RLIP76 to be developed as a therapeutic agent for kidney cancer. In the present review, we discuss the mechanisms underlying apoptosis caused by RLIP76 depletion, the role of RLIP76 in clathrin-dependent endocytosis deficiency, and the feasibility of RLIP76-targeted therapy for kidney cancer.
Keywords: RLIP76; chemotherapeutics; drug-resistance; glutathione-conjugate transport; kidney cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Atkins MB, Ernstoff MS, Figlin RA, Flaherty KT, George DJ, Kaelin WG, et al. Innovations and challenges in renal cell carcinoma: summary statement from the Second Cambridge Conference. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;2:667s–670s. - PubMed
-
- Linehan WM, Vasselli J, Srinivasan R, Walther MM, Merino M, Choyke P, et al. Genetic basis of cancer of the kidney: disease-specific approaches to therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:6282S–6289S. - PubMed
-
- Costa LJ, Drabkin HA. Renal cell carcinoma: new developments in molecular biology and potential for targeted therapies. Oncologist. 2007;12:1404–1415. - PubMed
-
- Shukla S, Wu CP, Ambudkar SV. Development of inhibitors of ATP-binding cassette drug transporters: present status and challenges. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2008;4:205–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

