The role of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway in human cancers induced by infection with human papillomaviruses
- PMID: 26022660
- PMCID: PMC4498560
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-015-0361-x
The role of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway in human cancers induced by infection with human papillomaviruses
Abstract
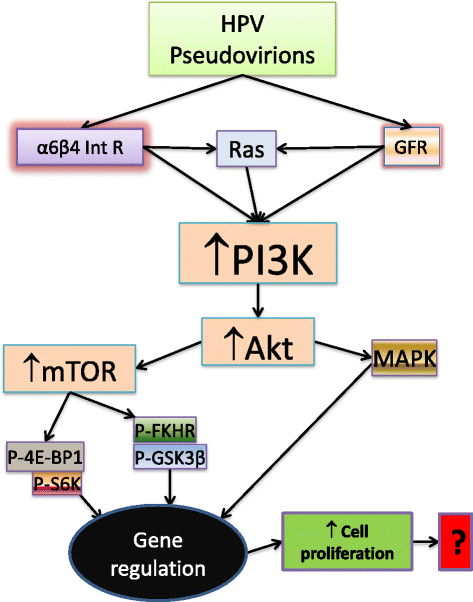
Infection with Human papillomaviruses (HPVs) leads to the development of a wide-range of cancers, accounting for 5% of all human cancers. A prominent example is cervical cancer, one of the leading causes of cancer death in women worldwide. It has been well established that tumor development and progression induced by HPV infection is driven by the sustained expression of two oncogenes E6 and E7. The expression of E6 and E7 not only inhibits the tumor suppressors p53 and Rb, but also alters additional signalling pathways that may be equally important for transformation. Among these pathways, the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling cascade plays a very important role in HPV-induced carcinogenesis by acting through multiple cellular and molecular events. In this review, we summarize the frequent amplification of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signals in HPV-induced cancers and discuss how HPV oncogenes E6/E7/E5 activate the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway to modulate tumor initiation and progression and affect patient outcome. Improvement of our understanding of the mechanism by which the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway contributes to the immortalization and carcinogenesis of HPV-transduced cells will assist in devising novel strategies for preventing and treating HPV-induced cancers.
Figures

References
-
- Zhao KN, Chen J. Codon usage roles in human papillomavirus. Rev Med Virol. 2011;21(6):397–411. - PubMed
-
- Gardiol D, Kuhne C, Glaunsinger B, Lee SS, Javier R, Banks L. Oncogenic human papillomavirus E6 proteins target the discs large tumour suppressor for proteasome-mediated degradation. Oncogene. 1999;18(40):5487–96. - PubMed
-
- zur Hausen H. Viruses in human cancers. Science. 1991;254(5035):1167–73. - PubMed
-
- Talora C, Cialfi S, Segatto O, Morrone S, Kim CJ, Frati L, et al. Constitutively active Notch1 induces growth arrest of HPV-positive cervical cancer cells via separate signaling pathways. Exp Cell Res. 2005;305(2):343–54. - PubMed
-
- Auvinen E, Crusius K, Steuer B, Alonso A. Human papillomavirus type 16 E5 protein (review) Int J Oncol. 1997;11(6):1297–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

