Reducing In-Stent Restenosis: Therapeutic Manipulation of miRNA in Vascular Remodeling and Inflammation
- PMID: 26022821
- PMCID: PMC4444526
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.03.549
Reducing In-Stent Restenosis: Therapeutic Manipulation of miRNA in Vascular Remodeling and Inflammation
Abstract
Background: Drug-eluting stents reduce the incidence of in-stent restenosis, but they result in delayed arterial healing and are associated with a chronic inflammatory response and hypersensitivity reactions. Identifying novel interventions to enhance wound healing and reduce the inflammatory response may improve long-term clinical outcomes. Micro-ribonucleic acids (miRNAs) are noncoding small ribonucleic acids that play a prominent role in the initiation and resolution of inflammation after vascular injury.
Objectives: This study sought to identify miRNA regulation and function after implantation of bare-metal and drug-eluting stents.
Methods: Pig, mouse, and in vitro models were used to investigate the role of miRNA in in-stent restenosis.
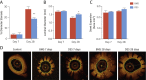
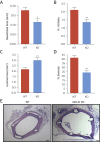
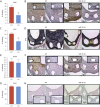
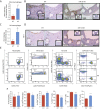
Results: We documented a subset of inflammatory miRNAs activated after stenting in pigs, including the miR-21 stem loop miRNAs. Genetic ablation of the miR-21 stem loop attenuated neointimal formation in mice post-stenting. This occurred via enhanced levels of anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages coupled with an impaired sensitivity of smooth muscle cells to respond to vascular activation.
Conclusions: MiR-21 plays a prominent role in promoting vascular inflammation and remodeling after stent injury. MiRNA-mediated modulation of the inflammatory response post-stenting may have therapeutic potential to accelerate wound healing and enhance the clinical efficacy of stenting.
Keywords: late stent thrombosis; miRNA stem loop; neointima; smooth muscle cell.
Copyright © 2015 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
Implementation of miRNAs to Reduce In-Stent Restenosis in the Future.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015 Jun 2;65(21):2328-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.04.008. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26022822 No abstract available.
References
-
- Serruys P.W., de Jaegere P., Kiemeneij F., et al. A comparison of balloon-expandable-stent implantation with balloon angioplasty in patients with coronary artery disease. Benestent Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:489–495. - PubMed
-
- De Bruyne B., Pijls N.H., Kalesan B., et al. Fractional flow reserve-guided PCI versus medical therapy in stable coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:991–1001. - PubMed
-
- Andersen H.R., Nielsen T.T., Rasmussen K., et al. A comparison of coronary angioplasty with fibrinolytic therapy in acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:733–742. - PubMed
-
- Serruys P.W., Kutryk M.J., Ong A.T. Coronary-artery stents. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:483–495. - PubMed
-
- Bavry A.A., Bhatt D.L. Appropriate use of drug-eluting stents: balancing the reduction in restenosis with the concern of late thrombosis. Lancet. 2008;371:2134–2143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

