Calcium-independent phospholipases A2 and their roles in biological processes and diseases
- PMID: 26023050
- PMCID: PMC4548770
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.R058701
Calcium-independent phospholipases A2 and their roles in biological processes and diseases
Abstract
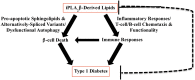
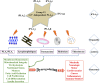
Among the family of phospholipases A2 (PLA2s) are the Ca(2+)-independent PLA2s (iPLA2s) and they are designated group VI iPLA2s. In relation to secretory and cytosolic PLA2s, the iPLA2s are more recently described and details of their expression and roles in biological functions are rapidly emerging. The iPLA2s or patatin-like phospholipases (PNPLAs) are intracellular enzymes that do not require Ca(2+) for activity, and contain lipase (GXSXG) and nucleotide-binding (GXGXXG) consensus sequences. Though nine PNPLAs have been recognized, PNPLA8 (membrane-associated iPLA2γ) and PNPLA9 (cytosol-associated iPLA2β) are the most widely studied and understood. The iPLA2s manifest a variety of activities in addition to phospholipase, are ubiquitously expressed, and participate in a multitude of biological processes, including fat catabolism, cell differentiation, maintenance of mitochondrial integrity, phospholipid remodeling, cell proliferation, signal transduction, and cell death. As might be expected, increased or decreased expression of iPLA2s can have profound effects on the metabolic state, CNS function, cardiovascular performance, and cell survival; therefore, dysregulation of iPLA2s can be a critical factor in the development of many diseases. This review is aimed at providing a general framework of the current understanding of the iPLA2s and discussion of the potential mechanisms of action of the iPLA2s and related involved lipid mediators.
Keywords: alternate splicing; arachidonic acid; cancers; central nervous system disorders; docosahexaenoic acid; eicosanoids; immune responses; inflammation; membrane homeostasis; signaling; β-cells.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Gijón M. A., Leslie C. C. 1997. Phospholipases A2. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 8: 297–303. - PubMed
-
- Wolf R. A., Gross R. W. 1985. Identification of neutral active phospholipase C which hydrolyzes choline glycerophospholipids and plasmalogen selective phospholipase A2 in canine myocardium. J. Biol. Chem. 260: 7295–7303. - PubMed
-
- Ramanadham S., Wolf M. J., Jett P. A., Gross R. W., Turk J. 1994. Characterization of an ATP-stimulatable Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 from clonal insulin-secreting HIT cells and rat pancreatic islets: a possible molecular component of the beta-cell fuel sensor. Biochemistry. 33: 7442–7452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

