The Relationship between Spontaneous Multi-Vessel Coronary Artery Dissection and Celiac Disease
- PMID: 26023313
- PMCID: PMC4446819
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2015.45.3.242
The Relationship between Spontaneous Multi-Vessel Coronary Artery Dissection and Celiac Disease
Abstract
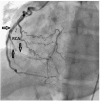
Celiac disease (CD) is an immune-mediated enteropathy involving the small intestines. Genetic and environmental risk factors as well as autoimmunity have been linked to its etiology. Studies have shown that coronary artery disease, autoimmune myocarditis, arrhythmias and premature atherosclerosis are more prevalent in individuals with CD compared to individuals without the disease. In this case report a young male patient with CD presented with acute myocardial infarction with spontaneous coronary artery dissections of two vessels. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case report of spontaneous multi-vessel coronary artery dissection in a patient with CD.
Keywords: Celiac disease; Dissection; Homocysteine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Green PH, Cellier C. Celiac disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1731–1743. - PubMed
-
- Schuppan D. Current concepts of celiac disease pathogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2000;119:234–242. - PubMed
-
- Collin P, Salmi J, Hällström O, et al. High frequency of coeliac disease in adult patients with type-I diabetes. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1989;24:81–84. - PubMed
-
- Rustgi AK, Peppercorn MA. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Intern Med. 1988;148:1583–1584. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources