Practice patterns in the management of threatened preterm labor in Korea: A multicenter retrospective study
- PMID: 26023669
- PMCID: PMC4444516
- DOI: 10.5468/ogs.2015.58.3.203
Practice patterns in the management of threatened preterm labor in Korea: A multicenter retrospective study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine clinical practice patterns in the management of pregnant women admitted with threatened preterm labor (TPL) in Korea.
Methods: Data from women admitted with a diagnosis of TPL were collected from 22 hospitals. TPL was defined as regular uterine contractions with or without other symptoms such as pelvic pressure, backache, increased vaginal discharge, menstrual-like cramps, bleeding/show and cervical changes. Data on general patient information, clinical characteristics at admission, use of tocolytics, antibiotics, and corticosteroids, and pregnancy outcomes were collected using an online data collections system.
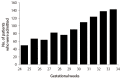
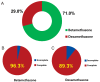
Results: A total of 947 women with TPL were enrolled. First-line tocolysis was administered to 822 (86.8%) patients. As a first-line tocolysis, beta-agonists were used most frequently (510/822, 62.0%), followed by magnesium sulfate (183/822, 22.3%), calcium channel blockers (91/822, 11.1%), and atosiban (38/822, 4.6%). Of the 822 women with first-line tocolysis, second-line tocolysis were required in 364 (44.3%). Of 364 with second-line, 199 had third-line tocolysis (37.4%). Antibiotics were administered to 29.9% of patients (284/947) with single (215, 22.7%), dual (26, 2.7%), and triple combinations (43, 4.5%). Corticosteroids were administered to 420 (44.4%) patients. Betamethasone was administered to 298 patients (71.0%), and dexamethasone was administered to 122 patients (29.0%).
Conclusion: Practice patterns in the management of TPL in Korea were quite various. It is needed to develop standardized practice guidelines for TPL management.
Keywords: Clinical practical pattern; Pregnancy outcome; Premature birth; Threatened preterm labor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapy side-effects and predictive factors for preterm delivery in patients undergoing tocolysis with atosiban or ritodrine for threatened preterm labour.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2014 Nov;34(8):684-9. doi: 10.3109/01443615.2014.930094. Epub 2014 Jun 24. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2014. PMID: 24959721
-
Controversies in tocolytic therapy.Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Dec;42(4):802-19. doi: 10.1097/00003081-199912000-00008. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1999. PMID: 10572695 Review.
-
[Tocolysis for preterm labor without premature preterm rupture of membranes].J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2016 Dec;45(10):1374-1398. doi: 10.1016/j.jgyn.2016.09.018. Epub 2016 Oct 28. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2016. PMID: 28029463 Review. French.
-
Management of threatened preterm delivery in France: a national practice survey (the EVAPRIMA study).BJOG. 2008 Nov;115(12):1538-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2008.01929.x. BJOG. 2008. PMID: 19035990
-
[Prevention of spontaneous preterm birth (excluding preterm premature rupture of membranes): Guidelines for clinical practice - Text of the Guidelines (short text)].J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2016 Dec;45(10):1446-1456. doi: 10.1016/j.jgyn.2016.09.011. Epub 2016 Nov 9. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2016. PMID: 27836377 Review. French.
Cited by
-
In utero exposure to ritodrine during pregnancy and risk of autism in their offspring until 8 years of age.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 13;11(1):1146. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80904-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33441922 Free PMC article.
-
How much have the perinatal outcomes of triplet pregnancies improved over the last two decades?Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2019 Jul;62(4):224-232. doi: 10.5468/ogs.2019.62.4.224. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31338339 Free PMC article.
-
Deleterious genetic variants in ciliopathy genes increase risk of ritodrine-induced cardiac and pulmonary side effects.BMC Med Genomics. 2018 Jan 24;11(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12920-018-0323-4. BMC Med Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29368655 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and side effect of ritodrine and magnesium sulfate in threatened preterm labor.Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2018 Jan;61(1):63-70. doi: 10.5468/ogs.2018.61.1.63. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29372151 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Microbial Communities During Pregnancy Are Associated With Preterm Birth.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jun 4;10:1122. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01122. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31214131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meloni A, Melis M, Alba E, Deiana S, Atzei A, Paoletti AM, et al. Medical therapy in the management of preterm birth. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2009;22(Suppl 3):72–76. - PubMed
-
- Haas DM, Imperiale TF, Kirkpatrick PR, Klein RW, Zollinger TW, Golichowski AM. Tocolytic therapy: a meta-analysis and decision analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:585–594. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

