Initial events in bacterial transcription initiation
- PMID: 26023916
- PMCID: PMC4496709
- DOI: 10.3390/biom5021035
Initial events in bacterial transcription initiation
Abstract
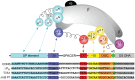
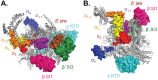
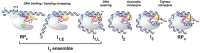
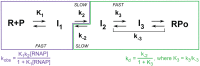
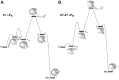
Transcription initiation is a highly regulated step of gene expression. Here, we discuss the series of large conformational changes set in motion by initial specific binding of bacterial RNA polymerase (RNAP) to promoter DNA and their relevance for regulation. Bending and wrapping of the upstream duplex facilitates bending of the downstream duplex into the active site cleft, nucleating opening of 13 bp in the cleft. The rate-determining opening step, driven by binding free energy, forms an unstable open complex, probably with the template strand in the active site. At some promoters, this initial open complex is greatly stabilized by rearrangements of the discriminator region between the -10 element and +1 base of the nontemplate strand and of mobile in-cleft and downstream elements of RNAP. The rate of open complex formation is regulated by effects on the rapidly-reversible steps preceding DNA opening, while open complex lifetime is regulated by effects on the stabilization of the initial open complex. Intrinsic DNA opening-closing appears less regulated. This noncovalent mechanism and its regulation exhibit many analogies to mechanisms of enzyme catalysis.
Keywords: RNA polymerase; kinetics; mechanism; promoter; transcription regulation.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

