Early treatment with metformin induces resistance against tumor growth in adult rats
- PMID: 26024008
- PMCID: PMC4623262
- DOI: 10.4161/15384047.2014.962968
Early treatment with metformin induces resistance against tumor growth in adult rats
Abstract
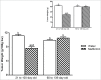
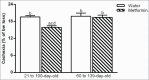
It is known that antidiabetic drug metformin, which is used worldwide, has anti-cancer effects and can be used to prevent cancer growth. We tested the hypothesis that tumor cell growth can be inhibited by early treatment with metformin. For this purpose, adult rats chronically treated with metformin in adolescence or in adulthood were inoculated with Walker 256 carcinoma cells. Adult rats that were treated with metformin during adolescence presented inhibition of tumor growth, and animals that were treated during adult life did not demonstrate any changes in tumor growth. Although we do not have data to disclose a molecular mechanism to the preventive metformin effect, we present, for the first time, results showing that cancer growth in adult life is dependent on early life intervention, thus supporting a new therapeutic prevention for cancer.
Keywords: AUC, area under the curve; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; HOMA-β, homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function; LBW, body weight loss; MHC-I, major histocompatibility complex class I; NAL, nasal anal length; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.; Walker 256 tumor; adolescence; antidiabetic; early treatment; metformin; prevention; tumor growth inhibition.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protective effect of metformin against walker 256 tumor growth is not dependent on metabolism improvement.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34(6):1920-32. doi: 10.1159/000366390. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 25500480
-
Metformin inhibits growth of thyroid carcinoma cells, suppresses self-renewal of derived cancer stem cells, and potentiates the effect of chemotherapeutic agents.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Apr;97(4):E510-20. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-1754. Epub 2012 Jan 25. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22278418
-
Use of biguanides to improve response to chemotherapy.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1165:3-9. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0856-1_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24839014 Review.
-
Combining metformin and nelfinavir exhibits synergistic effects against the growth of human cervical cancer cells and xenograft in nude mice.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 2;7:43373. doi: 10.1038/srep43373. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28252027 Free PMC article.
-
Combinational strategies of metformin and chemotherapy in cancers.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016 Jul;78(1):13-26. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-3037-3. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27118574 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Holistic Approaches for Overcoming Therapy Resistance in Pancreatic and Colon Cancers.Med Princ Pract. 2016;25 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):3-10. doi: 10.1159/000435814. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Med Princ Pract. 2016. PMID: 26228733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aerobic Exercise Training Attenuates Tumor Growth and Reduces Insulin Secretion in Walker 256 Tumor-Bearing Rats.Front Physiol. 2018 May 8;9:465. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00465. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29867528 Free PMC article.
-
Clenbuterol and metformin ameliorate cachexia parameters, but only clenbuterol reduces tumor growth via lipid peroxidation in Walker 256 tumor-bearing rats.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2025 Jan 31;58:e14060. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2024e14060. eCollection 2025. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2025. PMID: 39907424 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vatten LJ, Maehle BO, Lund Nilsen TI, Tretli S, Hsieh CC, Trichopoulos D, Stuver SO. Birth weight as a predictor of breast cancer: a case-control study in Norway. Brit J Cancer 2002; 86:89-91; PMID:11857017; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6600011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahlgren M, Sorensen T, Wohlfahrt J, Haflidadottir A, Holst C, Melbye M. Birth weight and risk of breast cancer in a cohort of 106,504 women. Int J Cancer J Int du Cancer 2003; 107:997-1000; PMID:14601061; http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijc.11481 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vickers MH, Gluckman PD, Coveny AH, Hofman PL, Cutfield WS, Gertler A, Breier BH, Harris M. Neonatal leptin treatment reverses developmental programming. Endocrinology 2005; 146:4211-6; PMID:16020474; http://dx.doi.org/10.1210/en.2005-0581 - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Oliveira JC, Lisboa PC, de Moura EG, Barella LF, Miranda RA, Malta A, Franco CC, Ribeiro TA, Torrezan R, Gravena C, et al. . Poor pubertal protein nutrition disturbs glucose-induced insulin secretion process in pancreatic islets and programs rats in adulthood to increase fat accumulation. J Endocrinol 2013; 216:195-206; PMID:23151360; http://dx.doi.org/10.1530/JOE-12-0408 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Innes K, Byers T, Schymura M. Birth characteristics and subsequent risk for breast cancer in very young women. Am J Epidemiol 2000; 152:1121-8; PMID:11130617; http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/aje/152.12.1121 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
