Biodistribution and function of extracellular miRNA-155 in mice
- PMID: 26024046
- PMCID: PMC4448655
- DOI: 10.1038/srep10721
Biodistribution and function of extracellular miRNA-155 in mice
Abstract
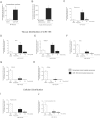
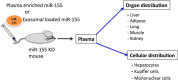
Circulating miRNAs can be found in extracellular vesicles (EV) and could be involved in intercellular communication. Here, we report the biodistribution of EV associated miR-155 using miR-155 KO mouse model. Administration of exosomes loaded with synthetic miR-155 mimic into miR-155 KO mice resulted in a rapid accumulation and clearance of miR-155 in the plasma with subsequent distribution in the liver, adipose tissue, lung, muscle and kidney (highest to lowest, respectively). miR-155 expression was detected in isolated hepatocytes and liver mononuclear cells of recipient KO mice suggesting its cellular uptake. In vitro, exosome-mediated restoration of miR-155 in Kupffer cells from miR-155 deficient mice augmented their LPS-induced MCP1 mRNA increase. The systemic delivery of wild type plasma to miR-155 KO mice also resulted in a rapid accumulation of miR-155 in the circulation and distribution to the liver and adipose tissue. In summary, our results demonstrate tissue biodistribution and biologic function of EV-associated miR-155.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exosomes derived from alcohol-treated hepatocytes horizontally transfer liver specific miRNA-122 and sensitize monocytes to LPS.Sci Rep. 2015 May 14;5:9991. doi: 10.1038/srep09991. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25973575 Free PMC article.
-
Increased number of circulating exosomes and their microRNA cargos are potential novel biomarkers in alcoholic hepatitis.J Transl Med. 2015 Aug 12;13:261. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0623-9. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26264599 Free PMC article.
-
miR-134 in extracellular vesicles reduces triple-negative breast cancer aggression and increases drug sensitivity.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 20;6(32):32774-89. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5192. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26416415 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-formed synthetic microRNA-143 is transferred to osteosarcoma cells and inhibits their migration.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Mar 7;445(2):381-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.02.007. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24525123
-
Evidence and potential in vivo functions for biofluid miRNAs: From expression profiling to functional testing: Potential roles of extracellular miRNAs as indicators of physiological change and as agents of intercellular information exchange.Bioessays. 2016 Apr;38(4):367-78. doi: 10.1002/bies.201500130. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Bioessays. 2016. PMID: 26934338 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical implications of exosome-derived noncoding RNAs in liver.Lab Invest. 2022 May;102(5):464-473. doi: 10.1038/s41374-021-00723-1. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Lab Invest. 2022. PMID: 35013531 Review.
-
Progress and prospects of long noncoding RNAs in lipid homeostasis.Mol Metab. 2015 Dec 29;5(3):164-170. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2015.12.003. eCollection 2016 Mar. Mol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26977388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alcohol Promotes Exosome Biogenesis and Release via Modulating Rabs and miR-192 Expression in Human Hepatocytes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 14;9:787356. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.787356. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35096820 Free PMC article.
-
Tagged extracellular vesicles with the RBD of the viral spike protein for delivery of antiviral agents against SARS-COV-2 infection.J Control Release. 2021 Jul 10;335:584-595. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.05.049. Epub 2021 Jun 3. J Control Release. 2021. PMID: 34089793 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular microRNAs as Biomarkers in Human Disease.Chonnam Med J. 2015 Aug;51(2):51-7. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2015.51.2.51. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Chonnam Med J. 2015. PMID: 26306299 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

